
1. First of all, what is polkadot? and what is parachain?
Polkadot is a protocol for other protocols. Polkadot builds its foundation on Web 3.0, the next generation of internet. It is a scalable multi-chain architecture where chains with varying functionalities can coexist and communicate among themselves in a security system that is shared among all chains. Polkadot provides a layer 0 relay chain where the environment can be shared between all the attached sharded parachains and bridges that run in parallel.
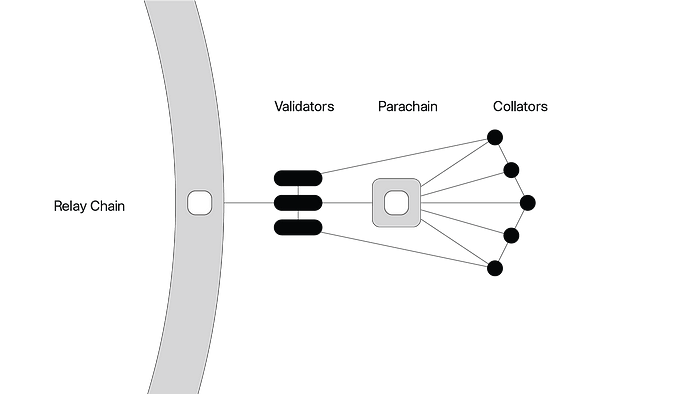
A parachain acquires its name due to its parallel relationship with the relay chain. It is an application-specific data structure that can benefit from scalability of the Polkadot system. Parachains are maintained by collators who maintain the network as full node operators, and blocks they produce are passed to the validators of the relay chain for verification.
A blockchain or an external system can interact with Polkadot either as a native parachain or a bridge parachain. A parachains is a constituent member of Polkadot, and projects can build on the Substrate framework enabling cost and development efficiencies. There is no need to build everything from scratch and also no need to operate a separate staker/miner incentivization mechanism. This is where Polkadot’s true value stems from. Each parachain is a self-sovereign simpler form of blockchain that its computations operate independently, but attached to the security and communication system of the relay chain. Theoretically, as the number of parachains increases, the performance of the work done can increase linearly using the same source without running into issues of collision.
2. Here’s why projects building on Polkadot should consider participating in the Parachain Slot Auction.
A blockchain system that tries to do everything on its own will probably fail to do any of them the best. Each chain can focus on things that they do the best as each parachain will have some specialization and customization such as smart-contracts, bridges, decentralized applications, services and even things that aren’t even out yet. Scalability can be achieved with enhanced performance by each constituent parachain doing its specialized one task the best. However, each logic doesn’t add too much value to the network if stood alone. The real-world value kicks in with interoperability, when each specialized entity can communicate and actually make use of each other.
There is a finite number of parachain slots that will gradually increase its number from its genesis stage. To ensure fairness in allocations and to pursue a market-based selection, slot leasing will take the form of an auction. Winners of the auction are free to deploy their parachains without the need for any permission, but slots will also have a finite lifetime. All the slots are available for projects to compete in, aside from a small number of slots reserved for what’s considered “common good” parachains administered by Web3 Foundation.
If a team does not need to lease a full parachain slot, parathread is available for temporary participation.
3. How does the Auction Work?
Since parachain slots are scarce, and they will be auctioned in a permissionless manner. Realistically, the Polkadot relay chain may support up to 100 parachains. The lease duration can be at most 2 years, broken into 3-month lease periods.The exact date for the first auction is decided by governance.
The slots are distributed by selecting winners of the candle auction mechanism. Here are some important things to note:
- Candle auction is an auction system that the participants cannot anticipate when the auction will end, just like how we don’t know when exactly the candle wick will burn out.
- In a traditional online candle auction, this is usually executed with a random number generation to decide when the auction terminates. Instead, in a parachain slot auction, there are known opening and closing phases.
- During the opening period, people have time to realize that there is an auction and also to place an initial bid. The bidding price can be increased as long as the auction is in an open phase.
- The ending period is fixed, but the auction can close any time during the ending period. The closing moment will be determined randomly, and the bidder with the highest amount at the closing moments wins the bid.
- After the entire ending period is run through, it is retroactively determined what the ending block is. Winner of that particular block becomes the winner of the entire auction.
This encourages a healthy way of projects determining the value of a parachain slot. Hopefully, this reflects what each project believes each slot is truly worth. The later bids will have less chance of winning because the retroactively determined closing moment may have been preceded the time of the bid submission. This prevents sniping, malicious block production, etc.
4. PLO Auction Participation
DOT or KSM is the asset that needs to be bond in the auction. Teams have to offer these for deposit to participate in the auctions and lease a parachain for a certain period of time. Bond tokens will be returned at the end of the lease. Tokens allocated to bond for a parachain slot cannot be staked. Teams pay for the slot auction with the expense of forfeiting staking rewards. The funds will be returned if the project loses the auction and the campaign ends or if the project wins and the lease expires.

To enter into a parachain auction with a personal account, the bidding team needs to have enough DOT/KSM tokens to lock for a certain period.
During the auction, DOT/KSM holders can bond their assets to support a project they believe should receive the slot, and the project provides rewards for the supporters. A project can also be crowdsourced for the support in the auction bid. DOT/KSM holders can bond these assets to Polkadot or Kusama network respectively, to alert the support.
