
sBTC — Unlocking Bitcoin to be a productive asset
Unlocking Bitcoin to be a productive asset

Table of Contents
- Introduction — Bitcoin and Financial Market
- Bitcoin Layers and $sBTC
- $sBTC Use Cases
- Limitations
- Summary
1. Introduction
Bitcoin is a network that successfully established a decentralized accounting system based on economic incentives, allowing anyone to participate. It still boasts the most decentralized node network and has proven that it can realize a strong accounting system without centralized intermediaries.
While other networks like Ethereum allow complex transactions, upgrading the system, Bitcoin remains faithful to the basics and boasts a stable accounting system. This should be the main force that $BTC can firmly maintains its position as the top market capitalization.
Furthermore, as the deleverging of financial market accelerated in 2022, numerous global cryptocurrency custodial institutions and centralized exchanges went bankrupt, and the Bitcoin community is raising the voice that this is a situation that occurred because it absolutely trusted centralized entities that create imbalances in information.
Therefore, instead of trusting someone, it is important to establish a system (1) in which assets must be directly owned, not custodial and (2) in which there is no need for trust in the first place and to maintain the permissionless decentralized accounting system stably, this most basic concept is receiving attention again.
1.1. The potential of Bitcoin
However, in this space that is obscured by good intentions of sticking to these basics, the question of whether a massive asset like $BTC really needs to just sit in non-custodial wallets continues to be raised.

$BTC recorded its highest market capitalization of $1.28 trillion in November 2021. This is an enormous value that far exceeds the peak of $0.22 trillion of the South Korean monetary base in July 2022.
Of course, Bitcoin, as a cryptocurrency born with a high level of security and value storage capability due to its minimalism of a single account and cash basis of accounting system, is well-known by all Bitcoin holders. However, human being have never left the existence of things that possess monetary value alone, but rather always turned them into tools of finance. In this world, the financial market has already developed based on the demand and supply between those who need money and those who want to make a profit by providing money, and therefore, money always has a time value.
It may seem contradictory to hold BTC for the purpose of earning interest. However, it is important to understand that there is a cost inherent in safely holding a liquid asset with monetary value, and therefore, it is necessary to hold it. Additionally, understanding the concept of this cost can also help us understand why there are constant efforts to incorporate Bitcoin into finance.
1.2. Risk Free Rate
Participants in modern economic activities will likely first think of interest rates as simply a concept where a variety of spreads are added on top of the base rates decided by central banks. However, fundamentally, interest rates are the value that one should be compensated with for choosing to consume in the future rather than in the present. People who have a greater benefit from consuming now will have a higher value that they should be compensated with in the future. This value is different for each person and macro condition. We refer to the value that simply rewards time preference, excluding all risk factors such as inflation, volatility, the possibility of bankruptcy, and other uncertainties, as the risk-free interest rate.
This can be simply represented mathematically as:

In short, the minimum opportunity cost for holding liquid assets with monetary value is the corresponding risk-free rate. Assuming that the ecosystem of Bitcoin holders is completely independent of the central bank’s base rate, until the establishment of Bitcoin’s own market rate, the position of Bitcoin holders is paying at least the compounding risk-free rates that vary based on their own characteristics and current market situation by paying the minimum risk-free return.
Of course, if the preference is to hold and pay at least the risk-free return, it is a rational investment decision.
In the concept of money supply and demand, the problem of holding costs is also included, and therefore, in the Bitcoin ecosystem, there is also a natural pressure for financial services to continue to emerge.
1.3. Bitcoin and Financial Market
As a result, financial services for Bitcoin have been continuously attempted so far and it is certain that they will continue to develop in the future.
However, in order to realize “finance” without centralized intermediaries in the Bitcoin network that adopts a single account and cash basis of accounting system, smart contracts must ultimately be used in separate layers.
Therefore, in order to guide Bitcoin holders who entered for the purpose of value storage and the benefits of high security through Bitcoin to the financial market, it will be necessary to meet several essential elements.
- In the case of using $BTC in other layers, it is important that the point of “owning” native Bitcoin rather than wrapping, which is based on the trust of the custodian, should not be compromised.
- Transactions must be supported by the security of the Bitcoin main chain.
As of January 23, 2021, the market capitalization of $BTC is $323B, while the market capitalization of $wBTC, which is commonly used in the Ethereum ecosystem with several basic DeFi infrastructure, is only $3B.
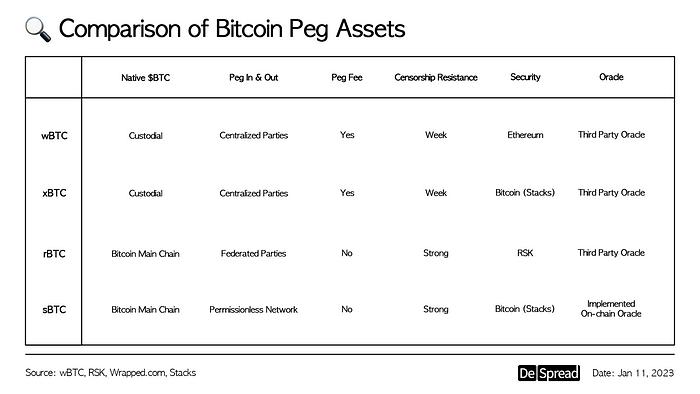
$wBTC, which is a token issued by centralized corporation BitGo, as collateral for native $BTC, does not meet the first requirement. If such a custodial institution goes bankrupt or its assets are seized by regulatory authorities for any reason, one $wBTC will not be able to receive one native $BTC.
In addition, transactions for $wBTC for financial purpose are smart contracts that occur on the Ethereum network, so it does not meet the second requirement.
Therefore, using $wBTC is considered as an action that gives up the true ownership of native $BTC, and using $wBTC is a risky action that cannot guarantee the most basic “Value Parity” and “Redeemability.”
In other words, if it does not meet the minimum two conditions mentioned above, the risk of exposing it to gain time value is excessively large for many Bitcoin holders, and they will not participate in Bitcoin finance.
For these reasons, the market capitalization of wrapped $BTC is very low compared to native $BTC. Of course, the Ethereum network has not yet implemented various financial services such as unsecured loan, but the current ratio of market capitalization of the two assets raises questions about the fundamental problem.
On the other hand, if financial services using $BTC that meet the above two conditions appear, the market capitalization and overall ecosystem of Bitcoin could greatly expand.
And currently, $sBTC is closest to presenting a solution for that.
This article was written based on information released on January 10, 2023, and at the time of writing, updates related to $sBTC and Nakamoto releases have not yet been implemented.
2. The Bitcoin layer and $sBTC
The bitcoin main chain emphasizes decentralization and security by minimizing speed and functionality. Therefore, the main chain is used for settlement and transaction finality, and a separate layer that interacts with the main chain is being developed to propose additional functions to the bitcoin network.
This separate layer is called “Bitcoin layer”, and the original Bitcoin is called “Bitcoin main chain”.
The most representative examples of the Bitcoin layer are the Lightning Network, which provides fast payments, the Liquid Network, which is for asset issuance, and the Stacks and RSK, which are for smart contracts.
When it comes to using Bitcoin in financial transactions, a fully expressive smart contract layer that supports accrual accounting is necessary. Additionally, this layer must allow for native $BTC to be traded without centralized intermediaries and transactions on this layer must be supported by the security of the Bitcoin network. Furthermore, this layer should not compromise “Value Parity” and “Redeemability.”
Unfortunately, current $BTC pegged assets for smart contracts other than the Bitcoin network do not meet these requirements.
And the solution that first proposed this is $sBTC, which is proposed by Stacks, the smart contract layer for Bitcoin.
2.1 First task: Cross-layer move and value peg of native $BTC.
Due to the fact that smart contracts cannot be executed on the main chain of Bitcoin, it is necessary to issue tokens on a separate layer that are linked to native $BTC so that Bitcoin holders can use them on the smart contract layer without losing ownership of the native $BTC.
The process of non-custodial collateralization of native $BTC must be done on the Bitcoin main chain (using Bitcoin script) before tokens are issued on the smart contract layer.
In this case, the Stack is the smart contract layer, and the tokens issued are $sBTC.
And it is important that the safety of the collateralized native BTC is guaranteed, and that “Redeemability” is achieved by allowing holders to redeem their $sBTC and receive their native $BTC at any time.
The collateral assets, native $BTC, exist on the Bitcoin main chain, and the collateralization process is also signed on the main chain. Stacks layer can read the signatures generated on Bitcoin, so the process of issuing $sBTC (peg-in) is not difficult. This is because Stack validators also run Bitcoin nodes and actively read and index the Bitcoin status.
What is important is that the redemption process does not result in an exploit and that all $sBTC holders can return to native $BTC (peg-out) is guaranteed. Stacks layer achieves this without relying on a centralized entity by leveraging its own unique consensus protocol, the proof of transfer.
The Bitcoin network established an economic incentive-based, permissionless accounting and auditing system through Proof of Work (POW), and in extension, Stacks layer also established an economic incentive-based, permissionless Bitcoin peg system through Proof of Transfer (POX). “Stackers” who participate in the POX and $BTC peg-in & out validations by burning $sBTC and releasing the same amount of collateralized native $BTC, and the structure induces correct validation based on economic incentives.
As a reward for correct validation, stackers receive native $BTC, but to attack the collateralized native $BTC through malicious behavior, a considerable amount of mining power and agreement from over 70% of stackers is required, which requires a huge amount of capital. Additionally, there is a limit on the issuance of $sBTC so that it does not exceed a certain percentage of the total value of the stacked assets, ultimately, the act of attack is designed to have no economic incentives.
Lastly, only Stacks can “signal the release of collateralized native $BTC” through a smart contract-based mechanism on the most decentralized and secure Bitcoin main chain. This feature is a unique advantage that allows for non-custodial peg-in & out of smart contract layer to be completed without intermediaries. This is thanks to the unique function of POX that allows smart contracts generated in Stacks to “Write” to the Bitcoin main chain.
Even $sBTC does not have to give up the strong censorship resistance of Bitcoin. Because signer selections, peg release requests, and other peg-related operations occur on the Bitcoin main chain, and they follow Bitcoin’s censorship resistance. In other words, even if Stacks is censored, the redeem of native $BTC cannot be censored.
Therefore, $sBTC of Stacks is currently the only form of $BTC peg asset issued in a smart contract-based, trustless, non-custodial manner, and it is one of the forms that most closely approaches the utilization of native $BTC in smart contracts. Therefore, it can be considered to have the strongest “Redeemability”.
Also, it can be seen that other $BTC wrapped assets adopt a method of verification by a custodian or centralized peg manager ($R-BTC, $L-BTC) based on trust, unlike $sBTC.

Additionally, POX method can independently fetch $BTC/$STX price pair information from the Bitcoin main chain during the consensus process. Therefore, Stacks’ consensus process includes a decentralized on-chain Bitcoin oracle that pegs the price of native $BTC to $sBTC without an external oracle. This means that it can achieve “value equality” stably without the burden of potential oracle attack risks.
2.2. Second Task: Transactions with the security of the Bitcoin main chain.
Even if assets can be safely transferred between the Bitcoin main chain and the smart contract layer, if there are security flaws in the smart contract itself, the redeemability may not be guaranteed.
Therefore, Stacks must provide at least the same level of security as the Bitcoin main chain when using $sBTC in smart contracts.
The solution to this task can also be obtained through POX.
Through the consensus of POX, all smart contracts and transaction hashes in Stacks verified are settled on the Bitcoin blockchain, and forks in Bitcoin are smoothly synchronized. As a result, transactions in Stacks have Bitcoin’s finality and are protected by Bitcoin’s hash power.
In conclusion, when exposing bitcoin to smart contracts for various functions, bitcoin holders do not have to give up the strong security of bitcoin.
In summary, by solving the two tasks described above, $sBTC and Stack for smart contracts realize the following:
“It is possible to interact with the bitcoin main chain and the smart contract layer in a non-custodial way, as close to native $BTC as possible, without intermediaries. Transactions that occur in this layer are supported by the security of bitcoin and do not compromise the redeemability and value parity.”
For more detailed information on peg-in & out and security rules, please refer to the sBTC and new stack white paper.
3. $sBTC Use Cases
3.1. Removal of Intermediary Costs related to Wrapping
$sBTC, unlike separate $BTC wrapped assets, does not incur additional expenses such as wrapping fees for issuance through the aforementioned decentralized non-custodial issuance method. Signature work for peg-in & out is carried out by receiving economic incentives ($BTC) from the proof-of-transfer consensus protocol, allowing for a structure that does not require additional fees. Therefore, by removing inefficiencies such as intermediary costs, value-added is already included in the $sBTC issuance mechanism.
For example, in the case of $wBTC, which currently has the highest market capitalization among $BTC wrapped assets, wrapping and unwrapping fees of 0.25% are imposed respectively. If the current (23.01.11) market capitalization of Bitcoin is $323 billion, it would result in $1.62 billion in fees each time it is wrapped and unwrapped, just by simple calculation. Additionally, as the market capitalization of Bitcoin and the use of smart contracts increase, these costs will also increase proportionally. However, $sBTC can completely eliminate these costs.
3.2. Smart Contracts
Above all, by safely utilizing the large and important asset of Bitcoin in smart contracts, $sBTC’s true meaning of existence is the ability to enable more modern transactions based on the accrual basis of accounting, not just simple transfers. This concept is significantly different from simple intermediary-based custodial single-ledger transactions.
However, currently, the dApps that provide smart contracts in the Bitcoin ecosystem, including Stacks, are still limited and there is still much room for development. As of January 2023, basic financial services such as over-collateralized stablecoin issuance for asset liquidity, money markets, and AMM have been implemented, and in the future, development of perpetual futures contracts, and partially collateralized Bitcoin lending platforms is in the development process.
Currently, the ecosystem where developers most actively participate in creating functions and services using smart contracts is undoubtedly Ethereum, and the Bitcoin layer is likely to follow this development trend. Of course, the emergence of the $sBTC system could trigger the value of native $BTC’s smart contract to be highlighted throughout the blockchain ecosystem, and the relationship could be reversed.

Additionally, the Bitcoin network alone can generate special financial demand that can be realized. Examples of exclusive finance related to the main chain can be seen by applying the hash power of simply POW, and it can be observed that it is already being traded on off-chain and Ethereum chains. In the Stacks, hash power itself can be used as a basic asset and financial and derivative transactions based on hash power can be created on-chain. And most importantly, the security of Bitcoin can be used to settle the transaction in the form of $sBTC, which is closest to the native $BTC, which is a unique feature.
Also, there are Bitcoin-related transactions that can only be implemented in the Stacks. Specifically, it is the process of POX which is unique to Stacks. Bitcoin holders can participate in “stacking”, which contributes to the Bitcoin layer for smart contracts and block creation related to $BTC-$sBTC, and receive native $BTC rewards. Although not yet implemented, if a liquid stacking like $stETH is realized, Bitcoin holders can contribute to the network without sacrificing their positions.
The most important thing is that the strength of the Bitcoin network, which no other ecosystem can follow, is that it is based on the most loyal basic principle of decentralization and has built a stable accounting system. And the impact that Bitcoin’s entry into the financial market will have on this society will be immeasurable.
Currently, $BTC boasts a market capitalization that rivals that of developed countries’ currency issuance, and the entry of this asset into the financial market will show a ripple effect of creating added value on a global scale through at least two of the following paths:
1. Increase in circulation leading to an increase in market capitalization
An increase in usage leads to an increase in the market capitalization of Bitcoin. According to the National Statistical Portal of South Korea, as of October 2022, the monetary base (M0) of South Korea is KRW 271 Trillion, compared to M2 that includes less than 2 years of deposit and MMF, is about KRW 3,753 Trillion, which is about 14 times. Of course, the financial services currently available on the Bitcoin layer cannot compete with the categories that traditional finance can provide, but it is enough to see that the introduction of financial market will lead to an increase in the market capitalization of Bitcoin.
2. Financial income proportional to the increased market capitalization
Additional value in the form of financial income from $BTC will occur as a result of the effective interest rate determined by an unspecified number of market participants. It is currently unclear to what extent the market rate will be set, but financial income arising from the national currency-like market capitalization (market capitalization) will undoubtedly correspond to an additional value that cannot be ignored.

4. Limitation
The current limitation proposed for $sBTC is that the total issuance of $sBTC, which corresponds to 60% of the total collateralized assets, is limited. However, the collateral ratio of 60% may be changed in the future through governance.
If the total amount of $BTC coming from the Bitcoin main chain ($sBTC’s market capitalization) exceeds the total amount of assets that collateralize the Stacks layer and $sBTC peg, someone may be motivated to seize the locked-up native $BTC by liquidating all the collateral assets. In other words, to prevent cases where the benefits obtained by distorting the system are greater than the losses, it is necessary to set a limit on the total issuance of $sBTC as described above, according to the Coase theorem.
During the gold standard era, when the demand for currency exceeded the total amount that could be issued, gold’s value could not rise as much as the demand for currency and instead the value of currency itself rose, resulting in deflation. We can think of this as similar to when the adoption rate of $sBTC exceeds the total issuance, the value of the Stacks platform may not increase as much as the demand for $sBTC. Of course, an increase in the adoption rate of $sBTC may have an impact on the value enhancement of Stacks itself, but the platform should develop more diverse value acquisition mechanisms to satisfy a sufficient amount of $sBTC issuance.
If it cannot be satisfied, inevitably trust-based wrapped assets such as $xBTC will have to be used in parallel.
Other limitations include, that for peg-out (returning to native $BTC), it requires an additional 150 blocks (about 24 hours) for Bitcoin to complete its finality and not to account for forks in the Bitcoin blockchain.
5. Summary
Bitcoin has built an accounting system that allow for only simple transactions and single account without intermediaries and has become the most decentralized accounting network successfully.
Therefore, there is no risk from external intermediaries and people can truly own valuable assets in non-custodial wallets under the motto of limited issuance and censorship resistance.
This has led to Bitcoin becoming a network with a high market capitalization and monetary value, leading to a surge in demand for financial services. However, the Bitcoin network itself does not support modern transactions, leading to custodial finance based on centralized intermediaries, which led to huge tragedy in 2022.
Ultimately, the need for decentralized, non-custodial peg-in and peg-out methods that maintain the security of the Bitcoin main chain and the ability to collateralize native $BTC without losing ownership has become more recognized.
And $sBTC and Stacks provide a solution for this. Of course, there is still much room for development in the dApp ecosystem on Stacks for modern and accrual based transactions. This is also connected to the task of enhancing the overall platform value of the Stacks and securing the total issuance of $sBTC, which must collateralize native $BTC.
Attempts at financial market through $BTC have been ongoing, both on and off chain. And the fact that finance through $BTC can bring a tremendous added value to the world is self-evident, and it will continue to be attempted in the future.
Stacks and $sBTC are the first to offer a decentralized, economic incentive-based peg-in and out system through smart contracts, without the need for a third-party intermediary. Additionally, this layer provides a unique consensus process called POX, which ensures that all transactions comply with the finality of Bitcoin, making it the only Bitcoin layer that does not compromise the security of Bitcoin.
As this model is implemented, we should pay attention to the high added value it can bring, and we will be able to observe the next phase of Bitcoin ecosystem.