1. Introduction
Cryptocurrency which was brought into sudden prominence in the investment asset world is showing its functional ability as a software that can offer various services without a centralized system based on a smart contract going beyond a simple money transfer and payment system. In particular, the decentralized finance (DeFi) market has been showing the most impressive advancement for the recent years, attracting the global capital. The market not only creates a basic financial market focused on currency minting・ deposit ・ borrowing ・ exchange ・ futures trading ・ automated market making, etc. but also dominates complex structured financial instrument such as trading separate tranches of securities and separate trading of interest strip / principal strips of securities.
As the crypto market consists of individual investors and a few crypto funds that are not subject to the regulation of the current capital market, the market cap and TVL are focused on finance protocols that are easy to understand and to access within the DeFi market.
However, investors in the crypto market will become smarter and more sophisticated meaning that the market will undoubtedly attract large institutional investors. Therefore, if there is any financial product which does not receive much attention from individual investors yet but is expected to see a surge in demand for institutional funds, one must follow up with the product.
One of such products is “options”.
2. Options
Most of the individual investors are not familiar with the options. In particular, the options products publicly available by brokerage firms are very limited, hard to understand, have non-user-friendly UI and difficult to trade because of a high Bid-Ask spread due to the lack of liquidity.
One can simply choose and purchase stocks of a company or index, while in case of options, one needs to pick a strike price and the expiration date and there are many others to consider. Therefore, in the options market in the traditional financial industry, most of the options trading are done by institutional investors that are armed with expertise, knowledge, and the economies of scale.
However, options products in the crypto market are different. The products have user-friendly UI that allows individuals to make a purchase with one click and there are various protocols ranging from those that are super easy to understand and those for smart money. Despite that, the products are still unfamiliar and that they are undervalued compared with the protocol revenue.
In addition, unlike individual investors, institutional investors must use options to manage a large amount of funds. Therefore, it can be said that protocols that belong to the options that are ignored even by the individual investors are highly likely to show substantial upside potential in the future.

For instance, Ribbon Finance, the leading on-chain option protocol has seen its revenue continue to rise since its launch on the mainnet, whereas its token price is moving into the opposite direction. And as of current April 8, 2022, its market cap only records around $ 57 million.
3. Options Overview
Before talking about the options protocols in the DeFi market, let us have a brief look at what options is.
Options is a contract to buy and sell a right. A buyer has a right to exercise and therefore exercises the option when he can make a profit and gives it up when he cannot make a profit.
On the contrary, the seller, when the other party exercises the option, has an obligation to respond to the buyer’s request.
Therefore, options that results in an asymmetric relationship between a buyer and a seller needs to be purchased, and the buyer needs to pay a premium.
Call options and put options are the two main types traded in the financial market.

- Call option: a right to buy an underlying asset at an exercise price on or before expiry (buyer exercises the option when the price of underlying asset is higher than the exercise price and profits from the difference)
- Put option: a right to sell an underlying asset at an exercise price on or before expiry (seller exercises the option when the price of underlying asset is lower than the exercise price and profits from the difference)
The two options are the basic types and one can take a long position and a short position in each option, meaning there are four categories that can be obtained.
1. Long Call Option = Call option buy position (long call) — call premium paid
2. Short Call Option = Call option sell position (short call) — call premium received
3. Long Put Option = Put option buy position (short put) — put premium paid
4. Short Put Option = Put option sell position (short put) — put premium received
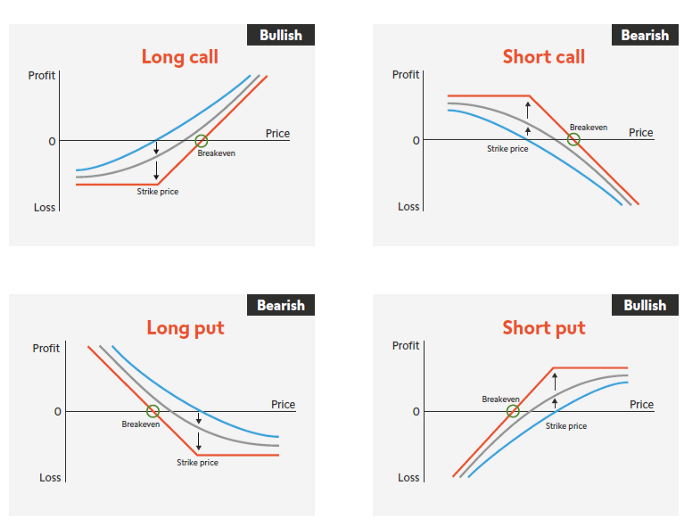
Orange graph refers to the P&L of the position on expiry, and when the current value of the underlying asset is lower than the strike price, an option is not exercised, meaning the P&L will not change further. However, due to the premium payment, an option buyer starts from the Loss whereas an option seller starts from Profit.
Curves in blue and gray refer to P&L that occur when the position is closed before the expiry (before losing the time value). There’s still time until expiry (in case of Long Position), so there’s an expectation that the price of the underlying asset will move in favor, and you can just decide not to exercise the option if the price moves in an unfavorable direction, which results in a curve that floats above (towards the Profit) the orange graph. Options is an asymmetric contract from the beginning, and when the price of an underlying asset either substantially goes down or up, either way benefits the options buyer than buying a spot underlying asset, so the value of options creates a convex P&L graph, and it can be expressed that the buyer has bought volatility in exchange of a premium and can also be called Long Gamma position. And the position, as it gets nearer to an expiry, converges to the straight-line orange graph.
The graph above is a P&L for naked options, and these four positions and underlying assets are combined to create numerous other positions.
Examples of long position criteria)
OTM: Out of the money (The exercise price that an option will not be exercised)
ATM: At the money (an option that has an exercise price that is the same as the current underlying asset)
ITM: In the money (The exercise price that an option will be exercised)
- Risk Reversal: long underlying asset + short OTM call + long OTM put
- Long volatility position (Straddle): long ATM call + long ATM put
- Long huge volatility position (Strangle): long OTM call + long OTM put
- Bull Call Spread: long ITM call + short OTM call
- Bear Put Spread: long ITM put + short OTM put
- Calendar Spread:
long call or put with far expiration date + the same exercise price short call or put with near expiration date
- Covered Call: long underlying asset + short OTM call
- Protective Put: long underlying asset + long put
- Cash-covered Put: cash on hand + short OTM put
Positions using options are more diverse than the examples above, and it is possible to reflect your trading perspective much more specifically into your position, or to change positions much more freely from a portfolio perspective than simply buying and selling spot assets.
However, the biggest problem is that buying and selling options can be complex unless you are a skilled trader or a portfolio manager. Questions that should be considered when trading options, including how the measured implied volatility that affects options price is, how the volatility skew of an option is, how to set an expiry and what would be the appropriate exercise price, will make one feel confused and lost.
Even worse, simple mistakes such as putting into wrong numbers or miscalculating the strike price could result in a significantly damaging loss.
Therefore, individual investors need a protocol that provides Vaults-type products that consist of options positions which are accessible with one click.
4. Ribbon Finance
Ribbon Finance is the first option products (Vaults) protocol on Ethereum.
Current offerings of Ribbon Finance include Vaults that exercise covered calls that utilize several underlying assets and cash secured put strategy using USDC as a collateral. At present it is hard to create various positions using options on chain as there are not enough counter parties to accept the options of Ribbon Finance. However, as the on-chain options market grows and the infrastructure to support the market is created, the options strategies to be offered by Ribbon Finance could exponentially grow, making them as one of the most-sought after options protocols.

This covered call is constructed by holding Ethereum as an underlying asset. User deposits its underlying asset $ETH to Vaults and the Vaults mints oToken in Opyn Protocol that offers infrastructure of on-chain options, using the $ETH deposited by the user.
oToken is an ERC20 token that contains a call options contract of the collateral asset, and buying the said token allows Vaults to take [$ETH(collateral) + short $ETH call position = covered call] position. An exception is $SOL where a call option issued at Zeta Markets. Please refer to the Docs of Ribbon Finance for more details about technical structure.
Vaults sells an ETH call option with expiry period of seven days and receives the call premium. Then, when the call option expires after seven days, it again sells another call option with expiry period of seven days, which repeats. And users of Vaults do not need to pay the gas fees for the rollover.
Also, as from the photo above, Vaults determines the exercise price of the call option each time and follows its method to set its own exercise price. According to Docs of Ribbon Finance, despite a short call position of crypto with high volatility, when the Ethereum rose from $80 to $2,000, only 5% of the options were exercised.
Likewise, Ribbon Finance has defined Theta Vaults (Theta means a type of Greeks that explains various matrix of options) as a strategy to add an additional yield to the underlying assets by earning a premium based on the options’ loss of time value (Time Decay).
Also, Ribbon Finance publicly disclosed that it is planning to launch Gamma Vaults (Gamma also a type of Greeks) product that creates a position using realized volatility of the underlying asset.
5. Squeeth

Squeeth is a protocol directly created by Opyn that leads the building infrastructure for DeFi options protocol by creating a short call position in Ribbon Finance.
To avoid any confusion, let me clarify the relationship between each protocol. Opyn protocol is a platform that provides an infrastructure where participants can create, buy, or sell on-chain options contracts created in the form of oToken (ERC20 token), and Ribbon Finance is a platform that utilizes the infrastructure to offer various position products in Vaults form to the users. And Squeeth is a protocol where Opyn protocol utilizes its resources to create options products which run on Squeeth.
Squeeth tracks the price of ETH^2 and has launched oSQTH that does not have an expiry and provides various options products by turning a volatility trading strategy into Vaults.
5.1. oSQTH
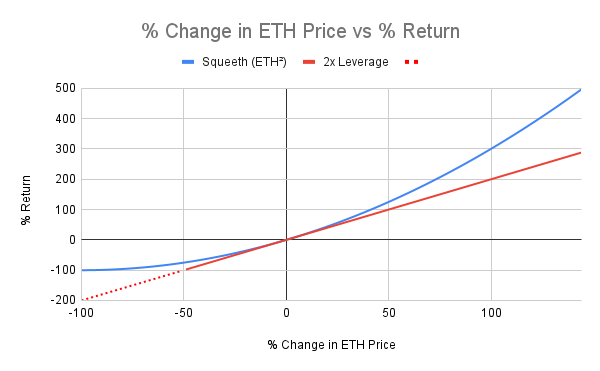
- Long oSQTH: Pay ETH and purchases ERC20 token called oSQTH.
The position is the same as constantly owning a long ATM call option with no expiry and is designed to gain as much as the square of the increase when ETH rises and fall below 2x ETH when ETH falls. What’s more, as the call option does not expire, even if the ETH’s price is lowered, Long oSQTH’s position will not be liquidated. Options is said to have convexity when you gain a lot more and lose a lot less and expressed as Long Gamma in Greek (long call P&L graph before the expiry). However, as it is the case with all options, the position with convexity comes with a price. Long oSQTH position will consistently have to pay the Short oSQTH position a call premium, which will be reflected in the way the price of the oSQTH token falls.
- Short oSQTH: Take an opposite position of Long oSQTH using ETH as a collateral.
This position is similar to keeping a short ATM straddle position that has no expiry and receives call premiums from Long oSQTH constantly.
However, when the price of ETH as underlying assets changes a lot, the price to pay to Long oSQTH gets bigger, and when the loss is more than the value of collateralized ETH, the collaterals will be liquidated, closing the position. It is a Short Gamma (buying volatility) position that is the opposite of the Long oSQTH and has a concave P&L profile.
For more details about each position, please refer to the relevant Opyn medium blog posts.
Reasons behind the emergence of these options products are as below.
1. Options whose expiry dates are different by even one day are completely different products, and this causes a problem that liquidity is distributed across each expiry.
Like the perpetual future was developed in the futures market, efforts were made to create options that have unlimited expiry to consolidate liquidity, which led to the creation of everlasting option.
2. However, options that have different exercise prices are also completely different, therefore consolidate the liquidity into a single instrument. => The emergence of Power Perpetual.
A position like ETH^p is called Power Perpetual, and options are constructed to have the same P&L as ETH² when the power is 2, and premiums higher than the Funding Rate of 2x ETH Perpetual should be paid, and the trader can take a Long Gamma position with the Convex P&L profile.
3. Turn the power perpetual position with power 2 into ERC-20 so that it can be easily bought by anyone. => The emergence of Squeeth (oSQTH).
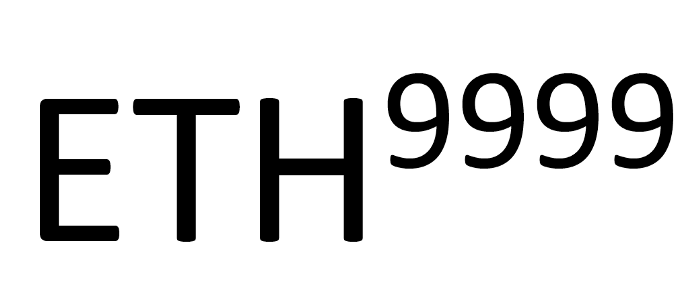
It is a very complex position as explained so far, however, you don’t need to either worry about how much to buy and sell, and how to set maturity and exercise price, and perform rollover regularly.
A user can take Long/Short oSQTH positions with one click, on an options protocol Squeeth.
5.2. Crab Strategy
Squeeth is planning three Vaults of Bull strategy, Bear Strategy and Crab Strategy, and now only the Crab Strategy is active.

Crab Market refers to a sustained period in a financial exchange where the prices are range bound without changing into certain direction.
Under Crab Market, it is hard to create profits by simply buying or selling spots. However, in options market, there is a position that directly targets to gain profits when underlying asset prices are range bound.
It is an options strategy that consists of selling both ATM call option and put option of the same underlying assets and called short straddle strategy.
It is a typical strategy that is employed when there is volatility in the market, and the trader can make profits when the underlying asset price does not significantly change as seen from the graph above.
The premiums will be huge as two options are sold, and the trader expects the price won’t move dramatically so that he will receive bigger premiums than what he pays to the buyer.
To be clearer, a trader can make profits when the volatility created from the underlying assets actual movement until the expiry is smaller than the implied volatility reflected in the options price. Therefore, when the trader thinks the options price is set too high as the market anticipates excessively high volatility, he can sell the options and make profits.
Crab Strategy is similar to the short straddle strategy. However, it is designed as [long spot ETH + short oSQTH], not as a typical [short ETH call + short ETH put]. This design allows (1) the protocol to reliably increase the trading partner of Long oSQTH, (2) to take advantage of not having to seek the flexibility of the put option, and (3) to take the stability of the Vault by receiving spot ETH as collaterals from the user.
Crab Vaults does not use a put options strategy but create a sole Negative Gamma position by setting the Delta (another Greeks) to 0 for the amounts of short oSQTH and the long ETH. A user who wants the position can simply deposit ETH to the Crab Vaults of Squeeth protocol.
So far, we’ve briefly looked at what options are, and we’ve looked at Ribbon Finance and Squeeze, the leading option product protocols based on Ethereum. In the next episode, we will introduce the option platforms of various chains other than based on Ethereum and their features. In addition to these options Vaults protocols, there is also an options marketplace where cryptocurrency options can be traded on an on-chain orderbook, and we’ll talk about it in the further episode.
We’ve looked at some examples of the two protocols earlier, options allow you to reflect your trading perspective more freely into your position and manage portfolio more efficiently.
Even if individual investors are not familiar with the options products in the current crypto market, the fact that the options market is essential for the financial market remains unchanged. Crypto investors will continue to be smarter, and as the capitals of institutional investors flow into the market, the crypto options market will develop further.

