
StackingDAO — The Liquidity Magnet of Stacks DeFi
Focusing on the Role and Functions of StackingDAO

1. Overview of Liquid Staking Services
In blockchain networks that adopt a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm or similar mechanisms, such as Ethereum, staking a certain amount of native tokens is essential to participate in the block validation process. While staking enhances the security of the chain by tying up significant capital, it also introduces a trade-off: the capital locked up for staking cannot be used elsewhere, leading to lower capital efficiency.
Liquid staking was introduced as a solution to this trade-off, offering a service that allows staked assets to be liquefied, thereby participating in the block validation process without losing liquidity. Liquid staking services typically provide users with the following features to unlock the capital efficiency of staked assets:
- Tokenization of Staked Assets: When a user stakes assets through a liquid staking service, they receive derivative tokens (such as stETH) corresponding to the staked assets.
- Value Guarantee and Reward Distribution: The derivative tokens are guaranteed to be exchangeable 1:1 with the underlying staked assets. Holders of these tokens receive block validation rewards through mechanisms like rebasing or exchange rate adjustments.
- Liquidity and Asset Utilization: Users can leverage the value of derivative tokens in various decentralized applications (dApps), such as using them as collateral for loans or providing liquidity in DeFi activities.
Participating in block validation on certain chains comes with significant entry barriers. For instance, becoming an Ethereum validator requires a capital investment of 32 ETH (worth over $10,000), and Solana validators must bear high hardware costs due to the chain's demanding specifications.
Liquid staking services address these barriers by enabling broader user participation in the block validation process, yielding benefits for both the chain and its users. These benefits include:
- Increased Security: More native tokens are staked, strengthening the chain’s security.
- Enhanced Capital Efficiency: Users earn block validation rewards while utilizing the staked assets in DeFi activities.
1.1. The Role of Liquid Staking
Lido Finance, which launched in December 2020, is a pioneer of liquid staking services, particularly within the Ethereum ecosystem. Since the Ethereum Shanghai Upgrade in April 2023, which enabled withdrawals of staked ETH on the Beacon Chain, liquid staking services have gained renewed attention. Following the market recovery, the amount of ETH staked via liquid staking services has surged dramatically.
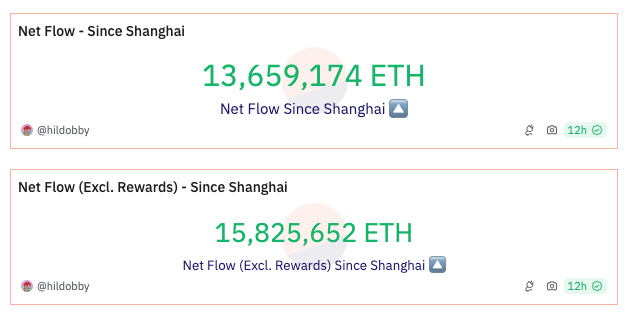
According to the Dune dashboard provided by hildobby, approximately 15.8 million ETH have been newly staked as of late July 2024, following the Shanghai upgrade. This amount surpasses the roughly 13.6 million ETH staked prior to the upgrade. Given that the Ethereum mainnet was launched in 2015, these figures indicate a sharp increase in demand for Ethereum staking over the approximately 15 months since the Shanghai upgrade. Additionally, about 32.6% of the current Ethereum staking volume is processed through liquid staking services, highlighting the significant role these services play in the on-chain ecosystem.
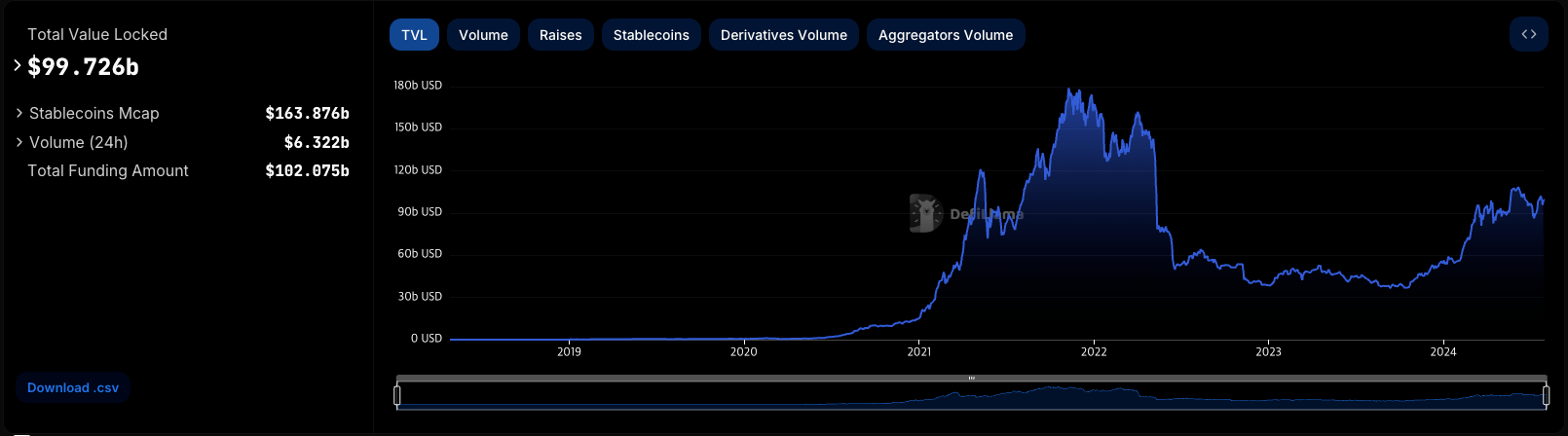
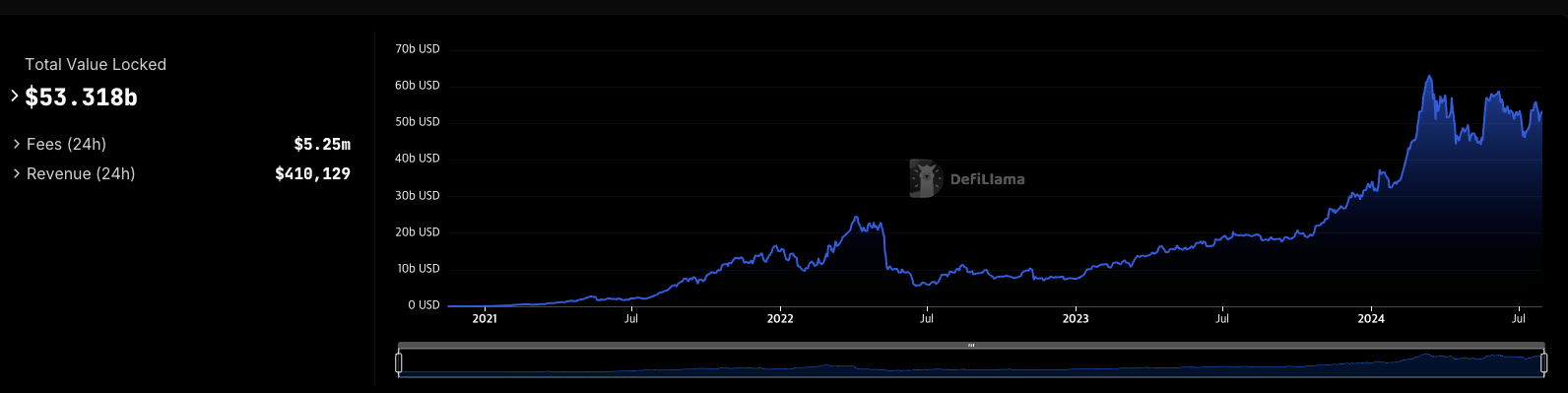
The rapid growth of liquid staking services is evident from their dominance, now accounting for over half of the total value locked (TVL) across all protocols (according to DefiLlama). Lido Finance alone boasts the highest TVL among all protocols, at approximately $32.7 billion.
Key Metrics as of August 1, 2024:
- Total TVL: $99.16 billion
- Liquid Staking Sector TVL: $50.7 billion
- Lido Finance TVL: $31.2 billion (Top among all protocols, with the second being EigenLayer at $15.5 billion)
- Ethereum Staking Volume: Approximately 34 million ETH
- Liquid Staking Utilization: Approximately 11 million ETH (32.6% of total ETH staked)
1.2. Applicability to Other Chains
The success of liquid staking services on the Ethereum chain has spurred their adoption on other chains, including Solana, Avalanche, and IBC-based chains. Several of these services have achieved significant TVL, proving their utility. Following Ethereum, Solana has become the second-largest chain in terms of liquid staking service operations, with notable protocols such as:
- Jito / TVL: $1.84 billion
- Marinade / TVL: $1.1 billion
- Sanctum / TVL: $758 million
These developments demonstrate the expanding influence of liquid staking services across different blockchain ecosystems.
2. Proof of Transfer (PoX) on Stacks and Liquid Staking
Even chains that do not adopt a Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism can create an environment conducive to liquid staking protocols if they involve a process where tokens are locked up or delegated to validators as part of their consensus mechanism. The Stacks blockchain, which uses the Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism, is an example of such a chain.
The PoX algorithm in the Stacks blockchain is characterized by the interaction between miners and stackers. Miners send Bitcoin (BTC) to stackers to gain the right to create Stacks blocks and earn STX rewards. Stackers, in turn, lock up a certain amount of STX and receive BTC rewards. For more detailed information, refer to the previously published report titled "Stacks — Advancing to the Next Stage Through Nakamoto Release."
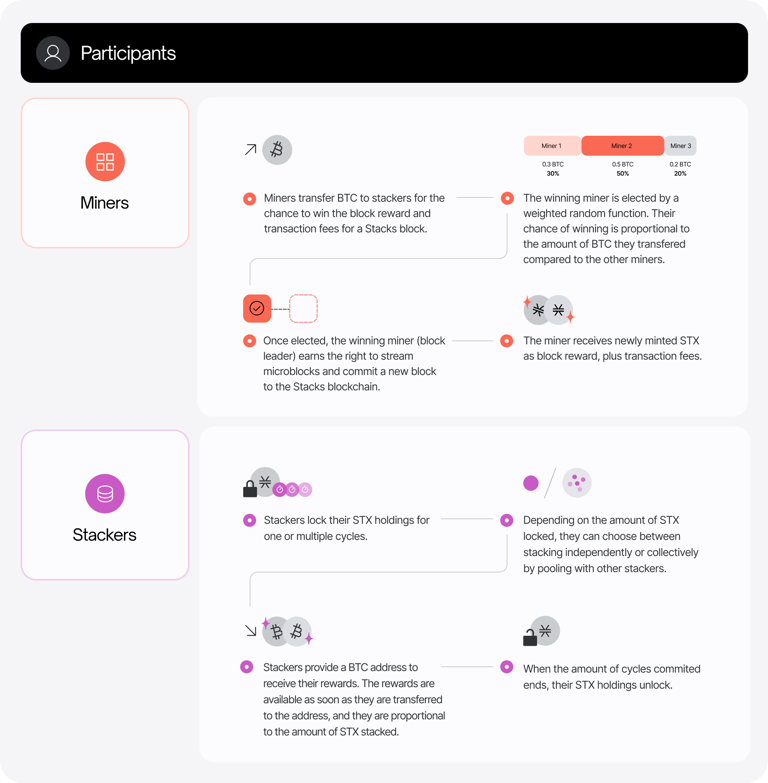
Initially, stackers could participate in the PoX process simply by locking up STX tokens. However, following the Nakamoto Release upgrade scheduled for the latter half of this year, stackers will take on a new role as signers. Signers will be responsible for validating, storing, signing, and propagating Stacks blocks produced during the miner’s term.
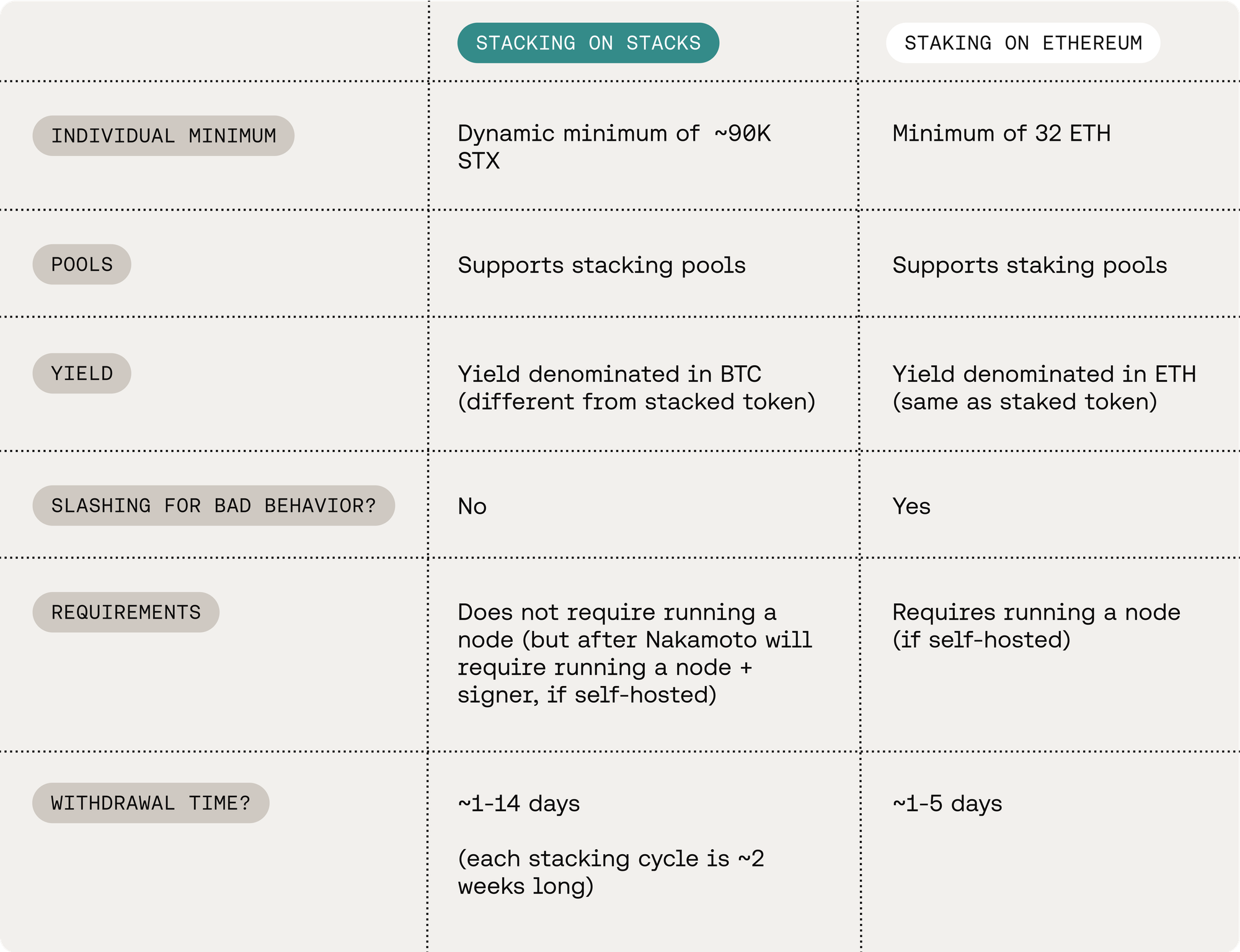
As shown in the diagram, the Stacking process in Stacks and the staking process in Ethereum share similarities in that: 1) both involve locking up tokens to participate in the chain's consensus mechanism, 2) both require a significant amount of native tokens and, in the case of Stacks after the Nakamoto Release, the operation of a node, creating barriers to entry, and 3) both require assets to be locked for a certain period, with withdrawal periods in place, leading to capital inefficiency, which underscores the need for liquid staking services.
3. Liquid Stacking Service: StackingDAO
3.1. Stacking Mechanism and the Role of StackingDAO
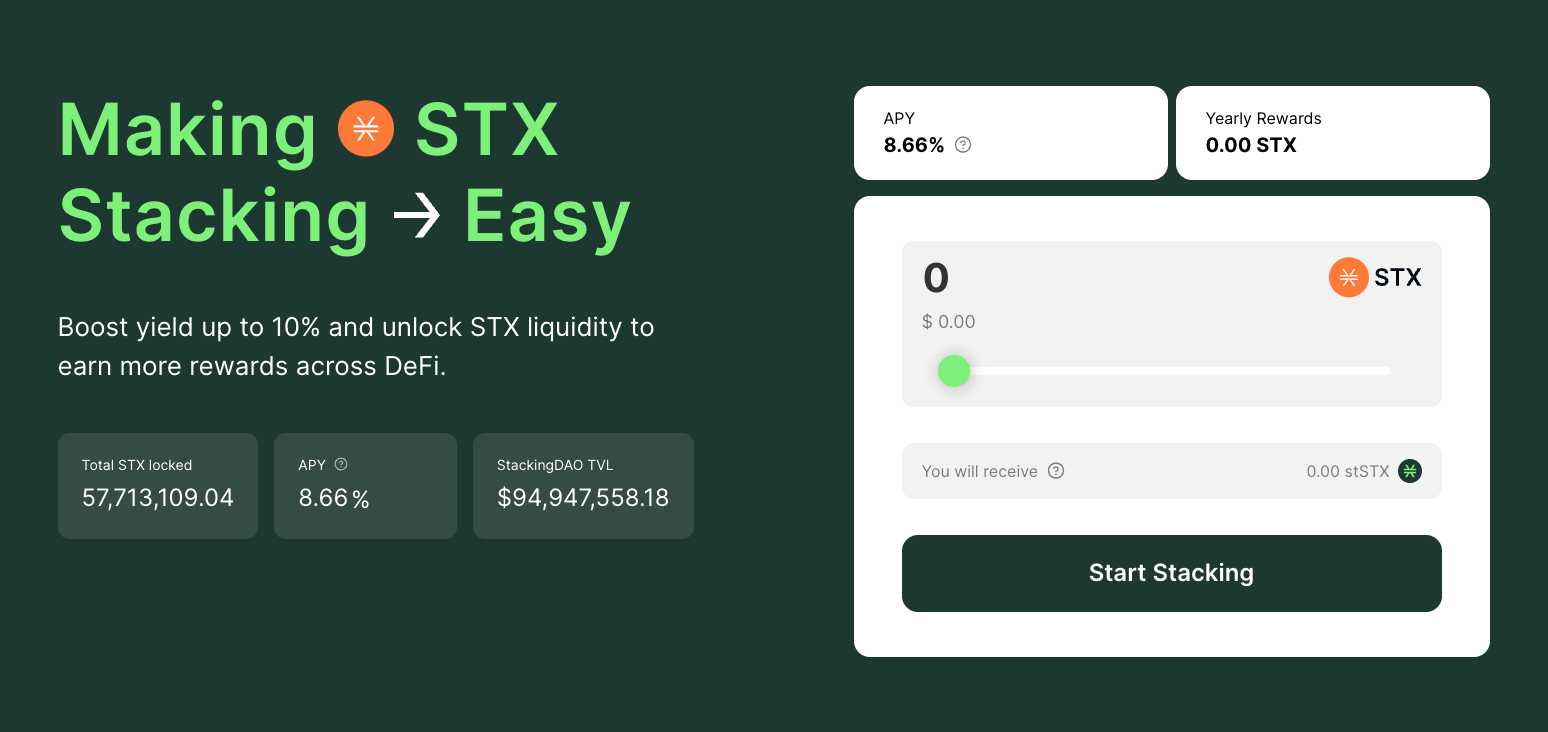
StackingDAO is a decentralized application (dApp) that offers liquid staking services for the Stacking process on Stacks. Similar to other liquid staking services, users can deposit their STX tokens into StackingDAO, participate in the Stacking process, receive derivative tokens called stSTX, and earn an annual percentage yield (APY) of around 8% (with a base of 7%).
The Stacking mechanism on Stacks shares similarities with Ethereum's staking process, which introduces several barriers to entry:
- Stacking Cycles: Stacking operates on a two-week cycle, leading to time constraints for locking, unlocking, and re-stacking.
- Minimum STX Requirement: A minimum of approximately 90,000 STX tokens is needed to register as a stacker.
- Node Operation: After the Nakamoto upgrade, stackers will also need to run nodes.
The two-week cycle presents a particular inconvenience for users who must lock and unlock their assets according to the cycle. Additionally, if a user wishes to unlock only a portion of their staked assets, they must unlock the entire amount and then relock the remaining portion, adding to the complexity.
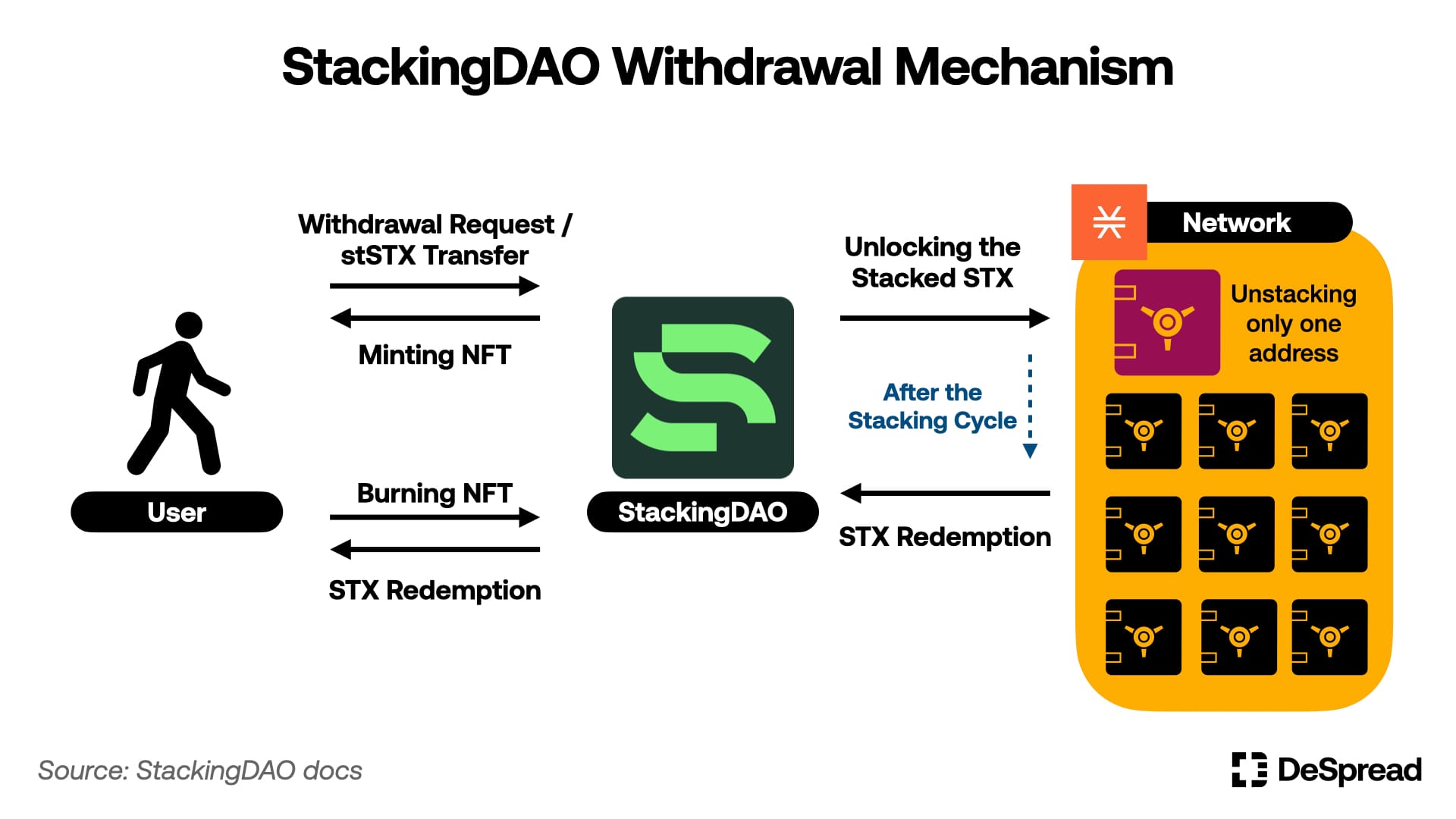
To address these challenges, StackingDAO has designed a withdrawal mechanism that lowers the barriers to entry while minimizing the impact on stacking yields. The key features include:
- Diversified Stacking Addresses: StackingDAO distributes STX across 10 different stacking addresses to mitigate yield impacts.
- Staggered Withdrawals: Only one of the 10 addresses is unlocked per stacking cycle, allowing for staggered withdrawals in response to user requests.
- NFT Issuance: When a user requests a withdrawal, they send their stSTX tokens to the protocol, which issues an NFT as a receipt. After the stacking cycle, users can burn the NFT to redeem their unlocked STX tokens.
This mechanism reduces the time constraints and inconveniences associated with the stacking process, ensuring that users can access their assets more flexibly while maintaining stacking yields.
3.2. Growth and Key Metrics
Liquid stacking just went live.
— muneeb.btc (@muneeb) December 18, 2023
Stacks (STX) has the unique property of earning native BTC payouts from consensus (at approx 6%). This creates a black hole effect. Why would I do anything else if I can earn BTC?
Now, with liquid STX (stSTX), people can have liquidity while…
Muneeb announcing the launch of StackingDAO, Source: muneeb X
Since its launch in December 2023, StackingDAO has quickly garnered attention by introducing a point system designed to attract users and capital. The point system rewards users daily with points based on their stSTX holdings, encouraging the pegging of stSTX and its use in DeFi protocols:
- 1 point per stSTX token held
- 1.5 points per stSTX token deposited in DeFi protocols
- 2.5 points per stSTX token deposited in Bitflow's stable swap pool
Key Metrics as of August 21, 2024:
- Total stSTX Issued: Approximately 56.8 million
- DeFi Utilization Rate of stSTX: 45%
- TVL of stSTX in DeFi: $36.78 million
- Total Points Issued: Approximately 14.95 billion
- Total Users: 37,498
StackingDAO, as the first liquid staking dApp in the Stacks ecosystem, achieved a peak TVL of nearly $125 million shortly after its launch. Despite market-wide corrections, it still maintains around $80 million in TVL, making it the dApp with the largest amount of capital in the Stacks ecosystem.
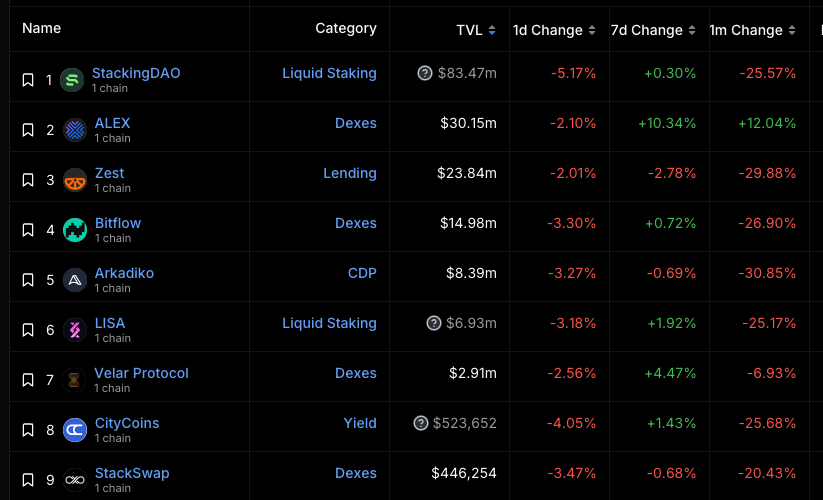
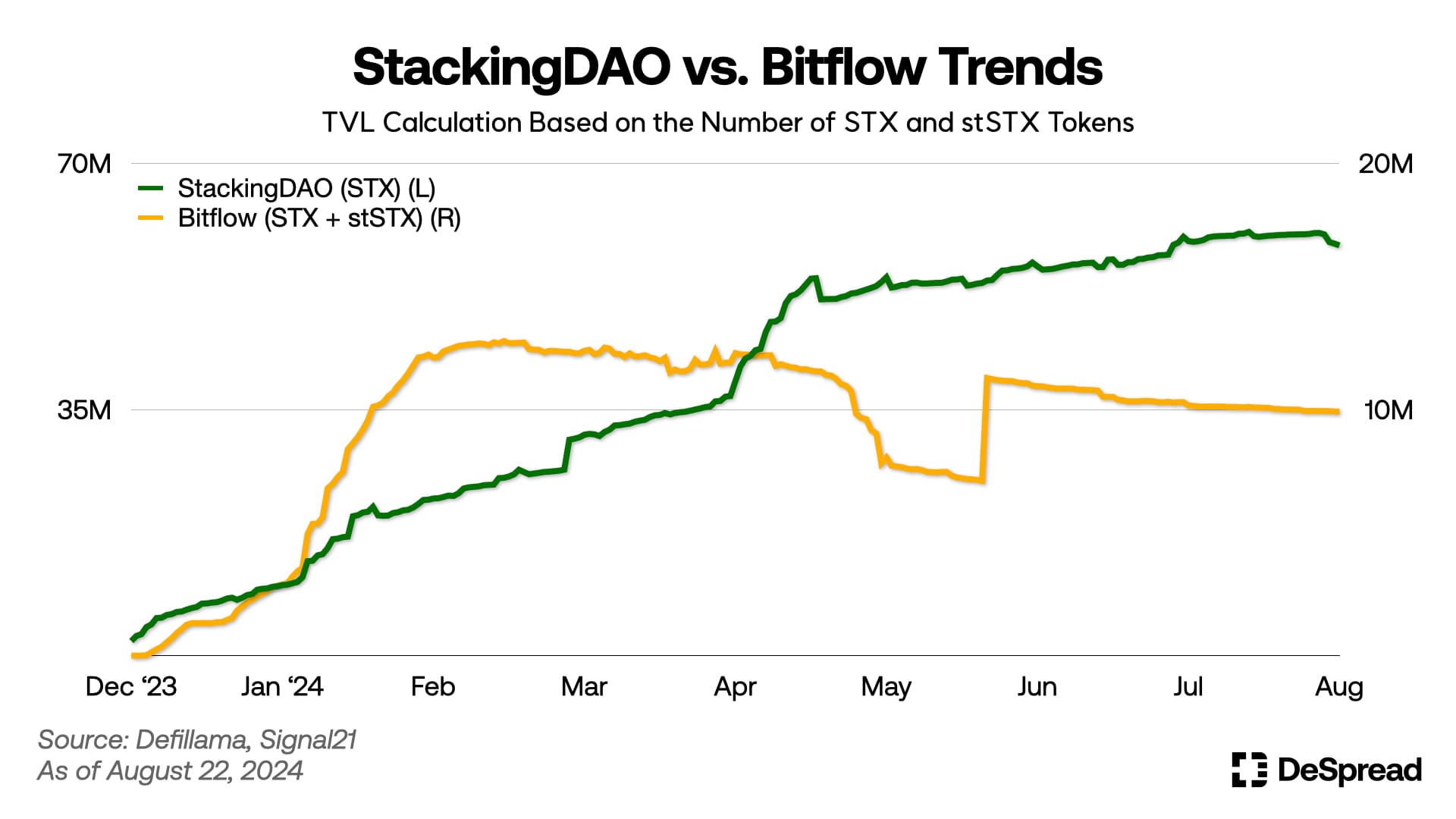
Bitflow, a protocol that offers a stableswap necessary for maintaining the value of stSTX, has also benefited significantly from the launch of StackingDAO and the introduction of the point system. Currently, about 10.5 million STX tokens are deposited in the protocol, highlighting its growth.
The TVL of StackingDAO, measured in STX tokens, has shown a consistent upward trend since its launch, with approximately 58.6 million tokens currently deposited. This represents about 4% of the total circulating supply of 1.48 billion STX and approximately 13% of the 425 million STX tokens currently involved in stacking, which is a substantial figure considering that the dApp is less than a year old.
3.3. Contribution to the Stacks Network: StackingDAO V2
Starting in late August, with the activation phase of the Nakamoto Release fully underway, stackers will transition into the role of signers responsible for validating Stacks blocks. This role is similar to that of validators in a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chain. Consequently, enhancing the stability and diversity of the signer network becomes a key objective for improving the security and decentralization of the Stacks blockchain post-Nakamoto Release.
In this context, StackingDAO has introduced StackingDAO V2, designed to streamline the onboarding process for new signers. A key feature of this update is the delegation of STX tokens deposited in StackingDAO to new signers on the Stacks blockchain, contributing to the growth of the network. This update was initially announced in March and was scheduled for implementation after the completion of the Nakamoto Release. However, following a delay, the delegation to the signer set was executed upon the completion of the instantiation phase in May 2024.
StackingDAO V2 is built around a mechanism where the STX tokens deposited by users are delegated in proportion to the performance of the signers. This design aims to achieve the following objectives:
StackingDAO V2 is designed with the following objectives:
- Network Performance Improvement: Delegating STX staking amounts to various signers to enhance the diversity of the signer network and incentivize signers to improve their performance.
- User Yield Enhancement: More STX staking amounts will be delegated to signers with higher performance, potentially offering users higher stacking yields.
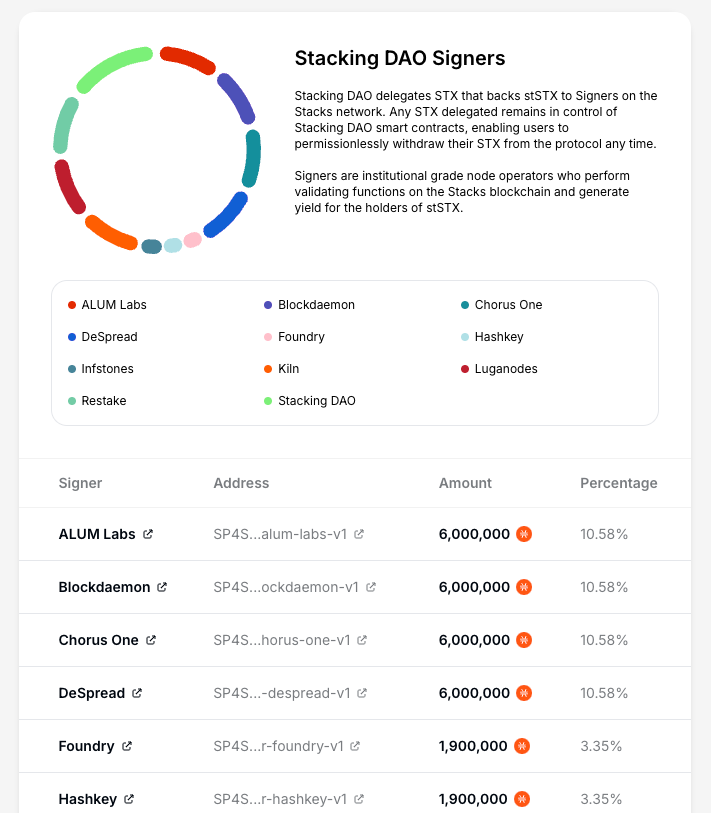
Even before the full activation of the Nakamoto Release, 10 entities (excluding StackingDAO) have already been onboarded to the StackingDAO signer program, with the delegation amounts distributed to these signers since May. Post-release, the onboarding of signers through StackingDAO is expected to expand, further enhancing the diversity of the signer network.
4. Conclusion
At the start of the year, amidst a surge of interest in the Bitcoin ecosystem, the Stacks network, alongside other projects, received significant attention. This attention propelled the network's total value locked (TVL) to a peak of $180 million in April—a remarkable 18-fold increase from the $10 million TVL recorded in September of the previous year.
However, the broader market soon entered a correction phase, compounded by several challenges within the Stacks ecosystem. These included a rescheduling of the Nakamoto Release and a hacking incident involving Alex, the ecosystem's leading decentralized exchange (DEX). Despite these setbacks, several emerging projects, including StackingDAO, Zest, Bitflow, and LISA, continued to accumulate TVL and show growth. With the Nakamoto Release update set to be completed by September, there is renewed optimism surrounding the future of the Stacks ecosystem.

As the Nakamoto Release comes to fruition, it will be interesting to observe how the ecosystem evolves, particularly the role of StackingDAO—the leading liquid staking dApp with the largest TVL. StackingDAO's journey to becoming a liquidity magnet within Stacks DeFi promises to be a critical development in the months ahead.
References
- Logan Lee, 스택킹다오 V2: 탄력적 네트워크 구성을 위한 사이너 지원
- StackingDAO, Stacking DAO V2: Bootstrapping the Stacks Validator Network
- StackingDAO, The Role of Stacks Signers and Stacking DAO For a Resilient Network
- StackingDAO docs
- Philip De Smedt and Niel Deckx, How Stacking DAO Uses NFTs to Create Withdrawal Receipts
- Signal21 Analytics
- Defillama
- Do Dive, 스택스 (Stacks) — 나비가 되려는 스택스의 나카모토라는 우화