
Chainlink 2.0 — Emerges as a Web 3 service platform
Highlighting Distinctions and Solutions

1. Introduction
Chainlink stands as a prominent decentralized oracle network, facilitating the exchange of data between on-chain and off-chain systems.It plays a crucial role in supplying real-world information to blockchain networks, finding applications across diverse sectors such as DeFi, NFTs, and gaming. As an indispensable solution for numerous projects, Chainlink’s impact continues to grow.
Currently, Chainlink operates on 16 blockchain networks, including Ethereum, BNB, and Arbitrum, with an on-chain value amounting to billions of dollars. However, the Chainlink team is not complacent.In April 2021, they unveiled the Chainlink 2.0 whitepaper, showcasing their aspirations to unlock the complete potential of the oracle network.
This article delves into Chainlink’s objectives for its 2.0 upgrade and examines the existing solutions it offers to revolutionize the blockchain industry.
2. Chainlink 2.0
In April 2021, Chainlink published a whitepaper called “Chainlink 2.0: Next Steps in the Evolution of Decentralized Oracle Networks,” marking a significant milestone in their development.Chainlink 2.0 is now operational, and it includes notable achievements such as the official launch of LINK staking on the Ethereum mainnet in December of the previous year.
The primary objective of Chainlink 2.0 is to enhance the connectivity, feature diversity, and scalability of off-chain systems by integrating them with on-chain functionalities through Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs). The aim is to minimize reliance on on-chain processes.Chainlink refers to this approach as “building hybrid smart contracts.”Now, let’s explore the concept of hybrid smart contracts and discover what sets them apart from traditional smart contracts.
2.1. Hybrid Smart Contracts
Hybrid smart contracts play a pivotal role in actualizing Chainlink’s vision of integrating on-chain and off-chain elements.Chainlink recognizes the importance of establishing a seamless connection between the on-chain component, which interacts with users on the blockchain network, and the off-chain component, responsible for aggregating and processing real-world data required by protocols offering services such as asset prices, weather information, and user data.By bridging these two realms, Chainlink aims to facilitate efficient and reliable access to external data necessary for the functioning of various blockchain-based services.
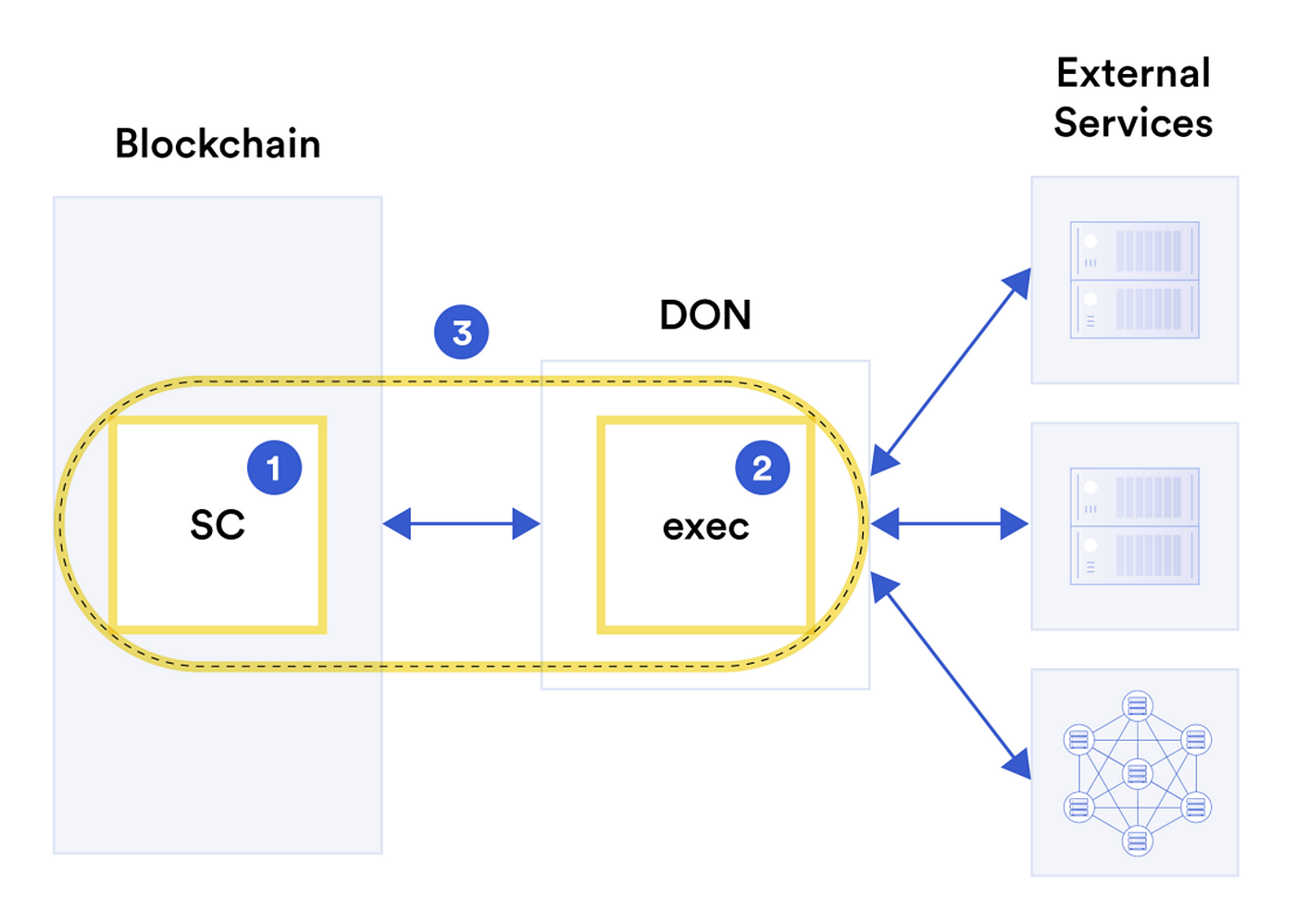
In the provided diagram, the contract is divided into two parts: part 1 (SC), which represents the on-chain component, and part 2 (exec), which represents the off-chain component. Chainlink refers to the combination of these two parts as a “hybrid smart contract”. With the Chainlink 2.0 update, they have enhanced the quality of their service by focusing on the following six items.
2.1.1. Abstracting away complexity
Chainlink has taken steps to simplify the intricate technical aspects of their platform, aiming to create a user-friendly interface that enables a broader range of developers to utilize their services. This approach is geared towards democratizing DONs. One of their key objectives is to provide a seamless onboarding process for traditional enterprises, allowing them to integrate their existing services onto the blockchain using Chainlink’s DONs, even if they lack expertise in blockchain development. By offering this bridge, Chainlink aims to facilitate the adoption of blockchain technology by traditional businesses, making it more accessible and inclusive.
2.1.2. Scaling
Chainlink 2.0 is specifically designed to cater to the expanding blockchain ecosystem, which has seen the emergence of numerous layer 1 and layer 2 solutions. In response to the growing demands, Chainlink focuses on reducing transaction processing time and minimizing fees (gas) through the implementation of off-chain computation.
Traditionally, oracle services transmit data from an external web server to an on-chain smart contract, where transactions and computations take place. However, in Chainlink 2.0, the process is modified. Upon receiving data from the web server, the oracle performs transactions and computations off-chain within the DON, and then sends the results back to the smart contract on the blockchain. In essence, by shifting the primary computation location from on-chain to off-chain, Chainlink has achieved scalability in terms of transaction processing speed and cost efficiency. This approach allows for faster and more cost-effective transaction processing, meeting the evolving needs of the blockchain ecosystem.
2.1.3. Confidentiality
DON nodes utilize zero-knowledge proofs to collect and process data without exposing sensitive user information. This protects privacy while allowing data to be used for new purposes. Enterprises can reduce reliance on trusting customer data, enhancing trust and privacy in data utilization.
2.1.4. Order-fairness for transactions
In the current blockchain landscape, users frequently encounter malicious attacks like front-running and sandwich attacks. To combat these issues and ensure fair transaction processing for regular users, transaction order fairness becomes crucial. Chainlink 2.0 introduces Fair Sequencing Services (FSS) as a solution to achieve transaction order fairness. Further details regarding FSS will be discussed in subsequent chapters.
2.1.5. Trust minimization
DON offers several measures to ensure user assurance. These include DON minority reports, which are submitted by select nodes in the DON when they detect fraudulent behavior. Guardrails are implemented to halt transaction execution when abnormal conditions are detected. Additionally, the use of public-key infrastructure (PKI) is employed to verify the identity of Chainlink network members, enhancing security and trust within the network. These information and security features contribute to user assurance and the overall integrity of the Chainlink ecosystem.
2.1.6. Incentive-based security
Finally, Chainlink 2.0 introduces LINK staking, enabling users to earn staking rewards while bolstering network security through “reward-based security.” This feature serves four key objectives:
1. Enhancing network security and user assurance
- In the event of a node failing to meet its on-chain Service Level Agreement (SLA) obligations, a portion of staked LINK is deducted and redistributed, reinforcing network security and user confidence.
2. Activating community participation
- LINK staking incentivizes increased direct engagement within the network.
- Participants can raise alerts when they detect oracle service failures against predefined performance criteria and receive rewards for valid and timely alerts.
3. Providing sustainable rewards for long-term participants
- With the rise in Chainlink’s usage, the associated fees collected also increase. This growth leads to higher rewards for stakeholders, ensuring sustainable incentives for long-term participation.
4. Building node reputation
- Protocols that stake more LINK as DON nodes earn greater trust from users. A higher staked amount signals increased reliability and strengthens the reputation of the participating nodes.
Through LINK staking, Chainlink aims to foster a more secure, participatory, and trusted ecosystem while providing sustainable rewards for long-term engagement.
3. Solutions provided by Chainlink 2.0
Chainlink’s official blog published their “Q1 2023 Product Update” on March 21st, where they unveiled the solutions they are providing to the blockchain industry.
3.1. Price Feeds
Chainlink has established itself as the standard for obtaining secure and reliable asset prices in the blockchain industry. Their price feeds, sourced from top data providers like CoinGecko and CoinMarketCap, have been trusted by numerous DeFi projects even prior to the Chainlink 2.0 upgrade. Currently utilized by 16 blockchain networks, these price feeds have facilitated over $7 trillion in transactions since 2022.
Building upon this success, Chainlink has developed a low-latency oracle that significantly improves the speed of information processing compared to traditional oracles. This advancement holds great potential for DeFi protocols, particularly derivatives protocols, as it helps overcome challenges such as price delays and front-running risks. By mitigating these issues, Chainlink’s low-latency oracle contributes to scaling the entire DeFi industry.
An example showcasing the practical application of Chainlink’s low-latency oracle is the collaboration with Coinbase Cloud to provide NFT floor price (FP) feeds.This demonstrates the real-world utilization and impact of Chainlink’s cutting-edge oracle solution.
In addition, GMX, Arbitrum’s leading decentralized exchange(DEX), announced a vote to use Chainlink 2.0’s low-latency oracles for its price feeds.
3.2. Chainlink Function
Chainlink Function serves as a developer platform within the Web 3 ecosystem, providing a serverless environment that empowers users to access external API data and write custom code on the Chainlink network. This platform, in collaboration with industry leaders like AWS, Meta, and the AP, simplifies the transition between Web 2 and Web 3 for developers by eliminating the need to manage infrastructure.With just a few lines of code, developers can seamlessly work with Chainlink Function to harness the power of external APIs and unlock the potential of Web 3.
Currently, Chainlink Function is in the beta phase on the Polygon Mumbai Testnet and the Ethereum Shepolia Testnet, allowing users to explore its capabilities and share their code on the official website. The website showcases notable examples of its usage, such as leveraging the Alphavantage API to access daily, weekly, and monthly US Treasury yields, or utilizing the Google Maps Distance Matrix API to obtain travel distance and time between two locations on a map. In essence, Chainlink Function enables users to extract data from Web 2 sources and freely customize it to suit their specific requirements within the Web 3 paradigm.
3.3. Proof of Reserve(PoR)
The incident involving FTX this past November brought attention to the significance of Proof of Reserves (PoR), which serves as an on-chain verification that a protocol safeguards its users’ assets. Chainlink plays a crucial role in offering dependable PoR by providing real-time updates of changes in off-chain reserves within on-chain contracts.
To illustrate, TUSD, the fifth-largest stablecoin with a market capitalization of around $2.1 billion, utilizes Chainlink PoR to manage token issuance. This involves ensuring that off-chain reserves are verified in real-time on-chain. Furthermore, prominent DeFi lending platforms like Aave and Benqi rely on Chainlink PoR to ascertain sufficient collateralization of bridged assets prior to enabling lending activities on the Avalanche network.
3.4. DECO
As mentioned earlier in the “Confidentiality” section, the objective of Chainlink 2.0 is to enable data collection and computation while preserving the privacy of users’ personal information. Introducing a novel solution to address this, Chainlink has developed DECO, a privacy oracle protocol. DECO enables individuals and organizations to establish, in a zero-knowledge state, the source of data transmitted to the oracle from a specific data provider. By implementing DECO, Chainlink aims to onboard a substantial volume of data currently residing in Web 2 APIs to Web 3 without compromising privacy, thus expanding the range of services offered. The application of DECO is planned across various domains such as credit scoring, KYC (Know Your Customer), healthcare, and fintech companies like Teller and Clique are presently testing services that leverage DECO.
3.5. Automation
Chainlink Automation is a solution designed to enable Web3 developers to automate specific smart contracts in a decentralized fashion.This implementation offers developers the advantage of saving time and resources in completing their projects while expanding the range of functionality by incorporating multiple Chainlink services.
The adoption of Chainlink Automation is widespread across various sectors, with a significant presence in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space. Prominent DeFi protocols like Aave, Synthetix, and Compound leverage this solution to automate processes such as liquidation, fee payments, and yield farming. This utilization streamlines asset movements, particularly in scenarios where repetitive actions are involved, enhancing operational efficiency within DeFi platforms.
3.6. VRF(Verifiable Random Function)
VRF is a solution designed to offer unbiased and tamper-proof on-chain randomness for applications built on blockchain technology. Randomness plays a critical role in various industries, including lotteries ($340B), video games ($200B), and the emerging sector of blockchain gaming ($5B). However, traditional methods of randomization often lack transparency, making it challenging to determine if the outcomes are genuinely random, necessitating trust in the protocol.
VRF addresses these concerns by providing on-chain randomization that eliminates the need for users to place blind trust in the system. It has found applications in diverse areas, ranging from NFTs to gaming. Currently, blockchain gaming and NFT projects like Gala Games, Planet IX, and CyberKongz are utilizing VRF. Chainlink has announced its commitment to further enhancing VRF, with a specific focus on advancing the technology within the blockchain gaming industry.FSS(Fair Sequencing Services)
3.7. Fair Sequencing Services (FSS)
FSS (Fair Sequencing Service) is a solution designed to ensure fair ordering of transactions and mitigate harmful attacks such as front-running and sandwich attacks, which can exploit the maximal extractable value (MEV) within the blockchain ecosystem. FSS achieves this objective by leveraging two fundamental characteristics of Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs):
- Secure causal ordering: This ordering mechanism involves sending transactions to a threshold-encrypted node, ensuring that the contents of the transactions remain undisclosed until the processing order is agreed upon. This approach enhances the security of transaction sequencing.
- Temporal ordering: FSS employs a first-in, first-out (FIFO) ordering method, guaranteeing that transactions entered into the oracle network are processed in the order they were received. This temporal ordering mechanism further reinforces fairness in transaction execution.
Currently, FSS is not publicly available, as it is undergoing proof-of-concept experimentation on the Ethereum Shepolia testnet. This testing phase allows Chainlink to assess the functionality and effectiveness of FSS in real-world scenarios before its wider release.
3.8. CCIP(Cross-Chainlink Interoperability Protocol)
The blockchain ecosystem is witnessing the emergence of numerous layer 1 and 2 solutions, and the interconnectivity between them is steadily increasing. By March 2023, the movement of assets between different chains had surpassed $170 billion, with a significant portion occurring in 2022 alone, accounting for approximately 70% of the total.
In this context, CCIP (Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol) plays a crucial role in fostering a multi-chain ecosystem.CCIP serves as a solution that facilitates the seamless transfer of messages and tokens across different chains. Moreover, it provides open-source standards that empower developers to easily and securely build cross-chain applications. Since October 2022, leading platforms such as Synthetix, Aave, and Qi DAO have been conducting cross-chain testing using an early alpha version of CCIP. Once fully commercialized, CCIP is expected to unlock a wide range of services for users, particularly within the realm of DeFi. These services may include cross-chain yield farming and collateralized lending, significantly expanding the possibilities and functionality of decentralized finance.Conclusion
4. Conclusion
Chainlink holds a significant position in the blockchain industry thanks to its distinct advantage of providing off-chain data. With the introduction of Chainlink 2.0, the objective is to empower individuals to utilize data in a more secure and efficient manner, without distinguishing between Web 2 and Web 3 environments. In their recent “Q1 2023 Product Update,” Chainlink unveiled several solutions, some of which are already in active use, such as price feeds and Proof of Reserves (PoR), while others are currently undergoing testing, including Verifiable Random Function (VRF) and Fair Sequencing Services (FSS). It will be intriguing to observe how Chainlink progresses along its roadmap and transforms these various solutions into practical tools in the future. Notably, their vision of becoming the industry-standard Web 3 services platform utilized by individuals worldwide holds great significance.
References
- Chainlink, Chainlink 2.0: Next Steps in the Evolution of Decentralized Oracle Networks, 2021
- Chainlink, The Chainlink Economics 2.0 Staking Protocol and Staking v0.1 Launch Details, 2022
- Chainlink, Chainlink Product Update: Q1 2023, 2023