
Hyperliquid — The Perpetual DEX Endgame
Focusing on hyperliquid's Structure and Ecosystem

1. Introduction
A Perpetual DEX (Decentralized Perpetual Futures Exchange) is a DeFi protocol that enables users to build leveraged positions for specific assets' upward or downward movements without expiration dates on the blockchain. Since November 2022, following the collapse of FTX, the world's second-largest centralized exchange, this DeFi sector has been steadily growing based on market participants' attention due to the emerging distrust in centralized exchanges.
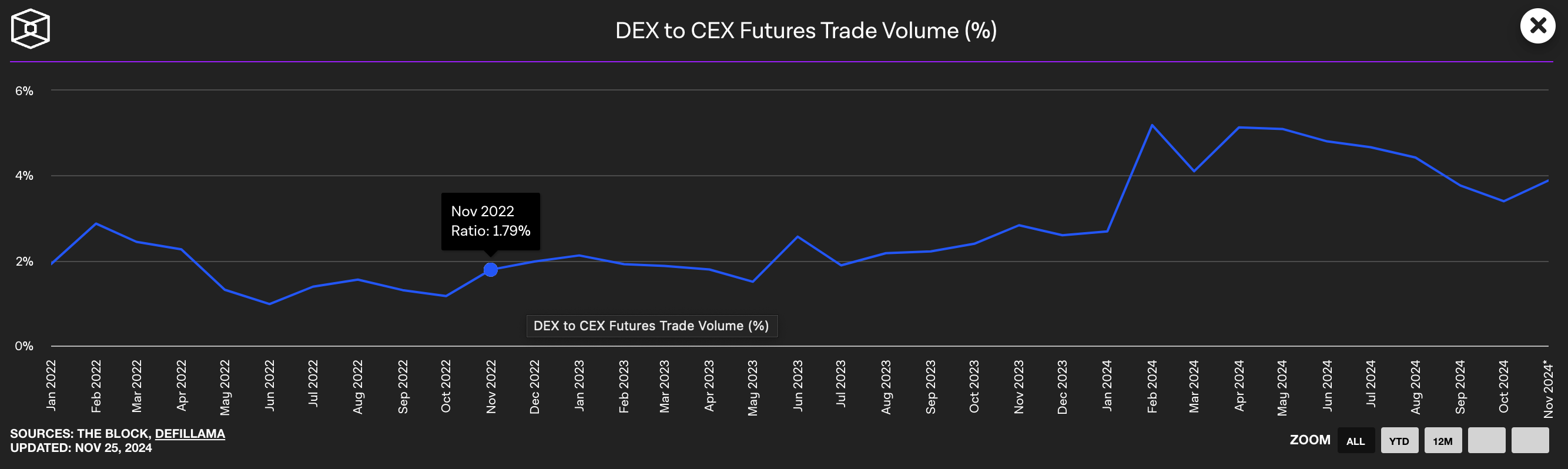
Existing Perpetual DEXes can be broadly classified into three models based on their price discovery mechanisms:
- Oracle Model: A model that operates based on external price data without its own price discovery. While it has the advantage that the protocol's liquidity size has minimal impact on traders' (takers') trades due to its reliance on external oracles, liquidity providers (makers) are exposed to single point risks and attacks from oracles, and the lack of its own price discovery mechanism limits growth (e.g., Jupiter)
- Orderbook Model: A model that utilizes the traditional capital market's bid/ask orderbook system. While traders can specify desired buy/sell prices making maker risk relatively low, it has limitations in efficient market maker activity due to blockchain block time constraints (e.g., dYdX)
- AMM Model: A model utilizing CPMM (Constant Product Market Makers), Uniswap's price discovery mechanism. Prices are determined according to specific formulas (e.g., X*Y=K) based on provided liquidity, and while it's easy to handle long-tail asset supply and demand without submitting or modifying orders to the orderbook, it inherently involves slippage in all trades (e.g., Perpetual Protocol)
1.1. Development and Limitations of Orderbook Perpetual DEXes
In the early development stages of Perpetual DEXes, oracle and AMM models were widely adopted in the market as they made it easier to secure liquidity needed for trading, since orderbook-based market makers found it difficult to operate efficiently due to blockchain's slow processing speeds and high fees. However, these models mostly faced a zero-sum game competing for limited liquidity while targeting only existing crypto market participants. Therefore, discussions and efforts to develop orderbook Perpetual DEXes continued to provide a familiar trading environment for traditional financial traders and achieve larger-scale growth based on their liquidity.
Recently, with the development of blockchain infrastructure such as Layer 2 and appchains, along with the introduction of methods that record only processed trades on-chain after receiving orders off-chain, the trading environment of orderbook Perpetual DEXes has seen significant improvements. Additionally, the development of orderbook Perpetual DEXes and related infrastructure continues with protocols such as:
- Vertex Protocol: A hybrid model Perpetual DEX that solved the problem of orderbook model Perpetual DEXes having relatively difficult liquidity bootstrapping compared to other models by mixing AMM and orderbook models
- Elixir: A protocol helping anyone easily execute liquidity provision in orderbook-type Perpetual DEXes
Despite these developments, orderbook Perpetual DEXes have not been able to present users with any differentiation beyond simply 'depositing' funds and creating 'positions' in the protocol. This has put them in a position where they cannot avoid direct competition with centralized exchanges, but they are at a competitive disadvantage compared to centralized exchanges due to the following two factors:
- Orderbook model Perpetual DEXes that process orders off-chain and only record results on-chain find it difficult to gain users' trust in terms of orderbook transparency
- Orderbook model Perpetual DEXes that operate completely on-chain require gas fees and signatures every time users submit trades, providing an inconvenient trading experience compared to centralized exchanges
Thus, current orderbook model Perpetual DEXes face a situation where they need infrastructure that can both optimize orderbook-based trading and build their own ecosystem to create network effects. In this context, Hyperliquid has emerged with a vision to become a fully transparent and user-friendly 'on-chain Binance' by complementing the above issues.
2. Hyperliquid, A Protocol for Hyperliquidity
Hyperliquid is a high-performance Layer 1 optimized for orderbook trading that processes 2 million transactions per second, and it launched in June 2023 with the team's own capital without external investment capital.
At the core of Hyperliquid is a native Perpetual DEX in orderbook form where all procedures from order submission to trade execution are recorded on-chain. While Hyperliquid DEX records all user activities on-chain, it provides convenience features such as creating trading accounts via email and not requiring separate signatures or gas fees for submitting trades, offering a user experience comparable to centralized exchanges.
With these distinctive features, Hyperliquid has grown steadily since its launch, achieving $2.14b in net fund inflows as of December 11, 2024, with monthly trading volume of $77b and open interest of $3.37b as of November, which is about 4 times higher than Jupiter's open interest of $815M, the second-highest in trading volume, leading among orderbook model Perpetual DEXes.
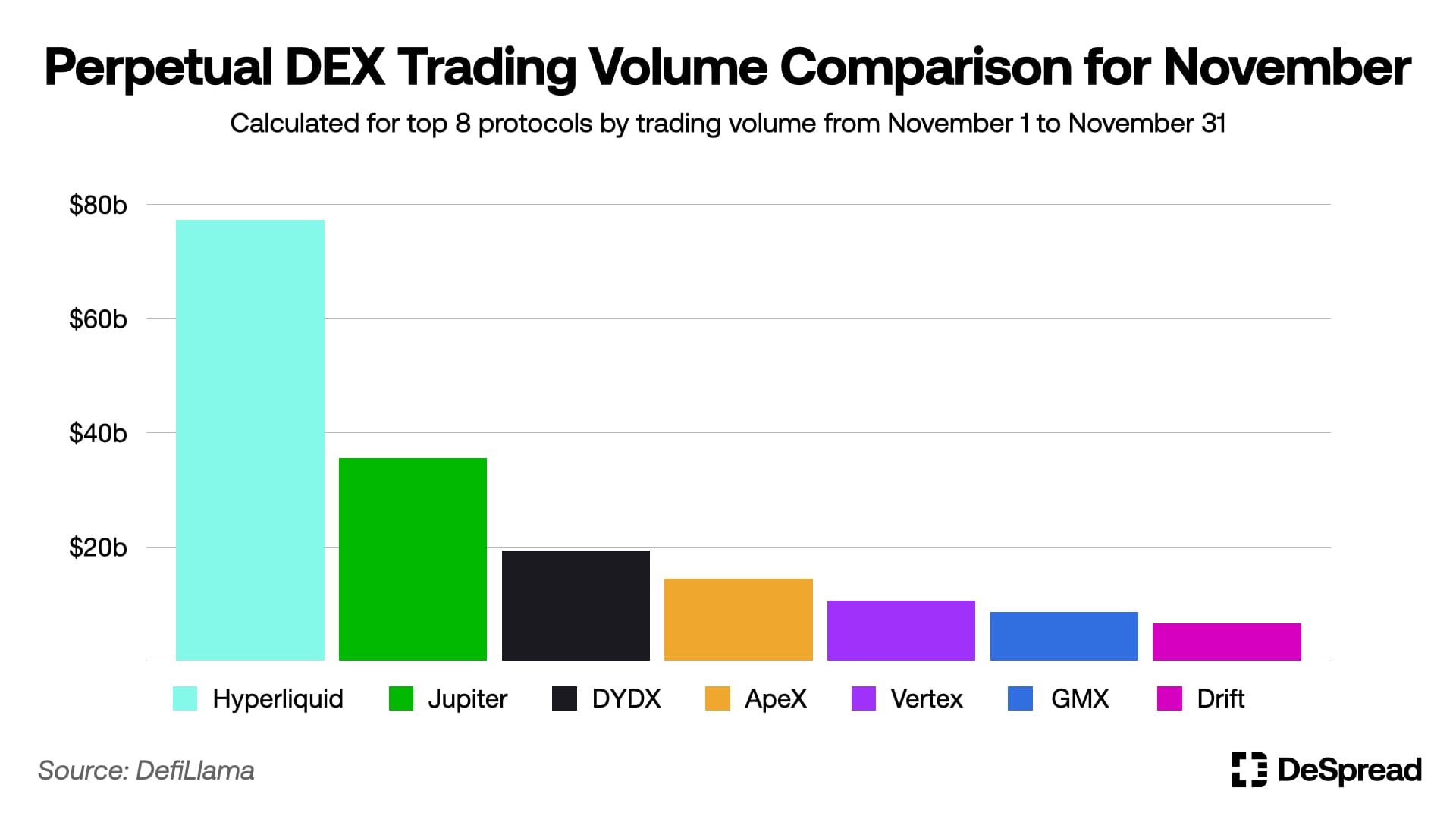
Let's examine Hyperliquid's components and operating mechanisms in more detail.
2.1. Hyperliquid Network
Originally at launch, Hyperliquid adopted Tendermint, Cosmos' consensus algorithm, instead of HyperBFT, considering interoperability with the Cosmos-based ecosystem and ease of deployment. However, the Tendermint consensus algorithm showed scalability limitations, only capable of processing around 20,000 orders per second. In response, the Hyperliquid team developed and introduced HyperBFT, their own consensus mechanism specialized for fast and high-volume trade processing, in May 2024.
HyperBFT is a model that further optimized the Hotstuff consensus algorithm, which is a more efficient improvement of the Tendermint consensus algorithm, specifically for Hyperliquid. While HyperBFT alone can theoretically process 2 million transactions per second, in actual operating environments, it can process up to 200,000 transactions with sub-second latency due to its combination with HyperVM (Rust language-based execution layer). This is one-eighth the TPS (Transactions Per Second) of Binance, a centralized exchange, but approximately 8 times higher than Injective, another protocol implementing an on-chain orderbook based on its own network.
Thus, Hyperliquid was designed and built around 'trading efficiency' and has the advantage that all orders submitted by users without gas fees are recorded and quickly processed on-chain. However, in a situation where there are no incentives provided to validators, the team currently operates all four nodes to ensure a fast order processing environment, raising questions from external sources about decentralization.
Aware of this, the Hyperliquid team is testing trustless node operation for validator decentralization on the testnet, and is also testing ways for anyone to participate in network validation by staking $HYPE, Hyperliquid's network token, even without directly operating nodes. To maintain a high-efficiency network state while securing decentralization, Hyperliquid has introduced a mechanism that transitions nodes that cannot maintain a certain level of performance to a 'Jailing' state, restricting them from proposing new blocks and participating in voting.
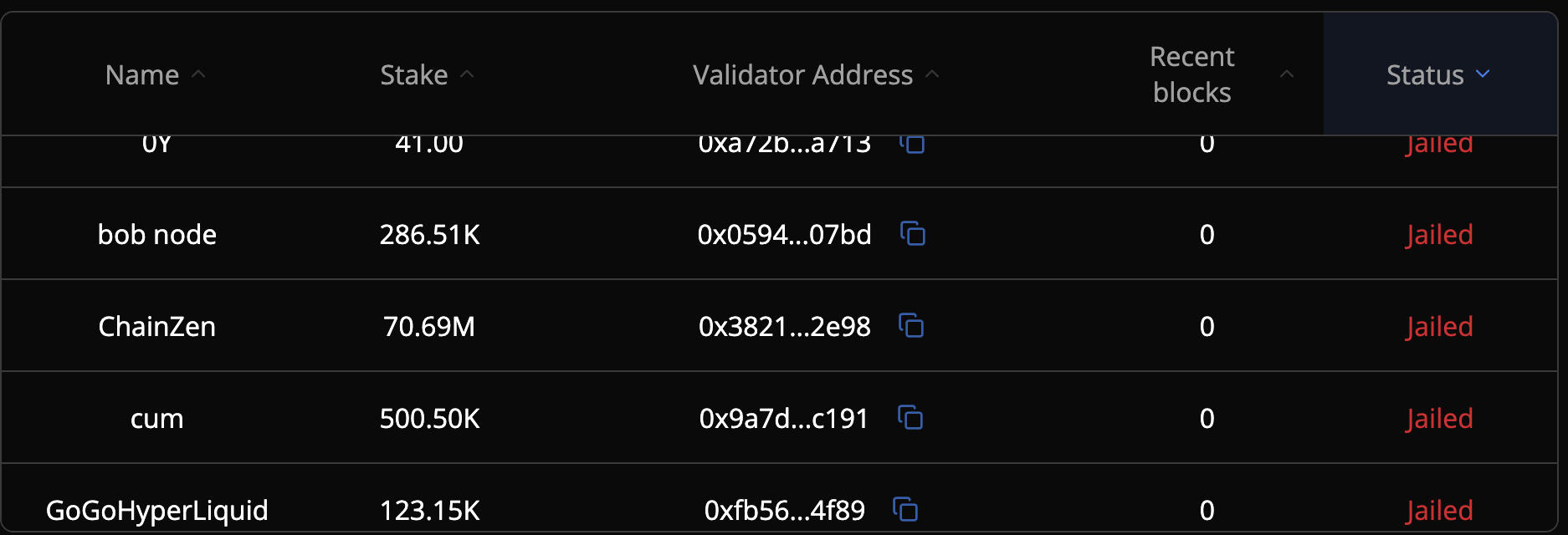
Additionally, the Hyperliquid team plans to introduce HyperEVM to work alongside the existing execution layer, HyperVM. This is expected to enable EVM-based applications to onboard into the Hyperliquid ecosystem and bridge ERC-20 tokens, and they plan to expand the ecosystem using these capabilities.
2.1.1. Hyperliquid Bridge
Users can deposit and lock stablecoins through the Hyperliquid Bridge, secured by Hyperliquid's validators, and receive the same amount of assets in their personal accounts on Hyperliquid to use the network and Perpetual DEX.
Currently, Hyperliquid only supports bridging USDC on the Arbitrum network. Recently, with increased market interest in Hyperliquid following the launch of its native token $HYPE, there has been a significant increase in users depositing assets, and we can see that net inflows to the Arbitrum network are notably higher compared to other networks.
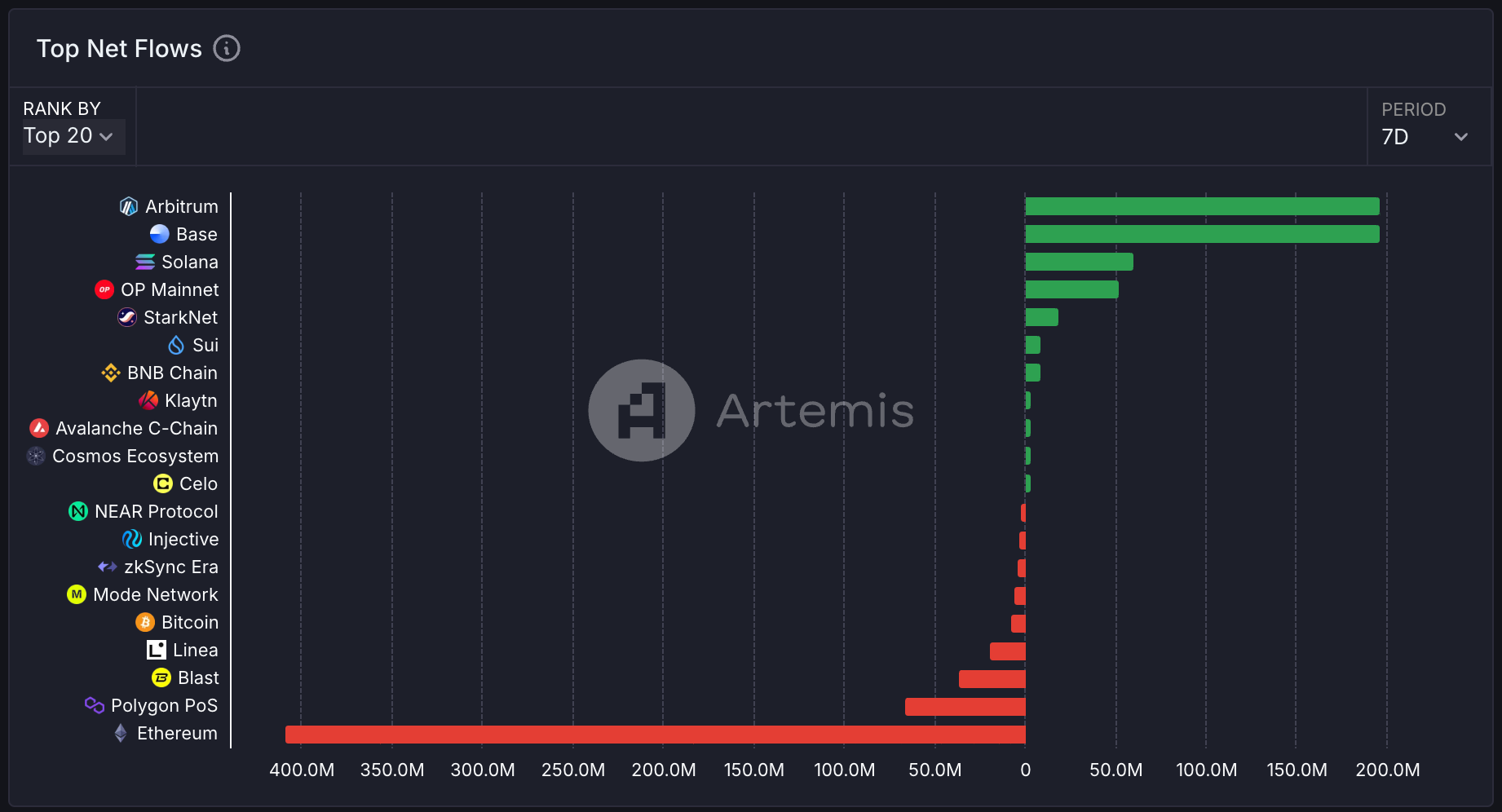
Currently, a fee of $1 is charged for withdrawals to cover gas fees on the Arbitrum network, and Hyperliquid plans to support bridging of various types of stablecoins from other networks besides USDC on Arbitrum in the future. In particular, after the launch of HyperEVM, it is likely to integrate with Circle's CCTP (Cross-Chain Transfer Protocol), which is expected to secure perfect interoperability with other networks for stablecoin transfers.
2.2. Hyperliquid DEX
As explained earlier, Hyperliquid DEX, operating on the Hyperliquid network with fast trade processing speed and no need for signatures and gas fees, provides a user experience almost identical to centralized exchanges and supports leveraged trading environments for over 100 different token pairs.
Hyperliquid DEX offers the following four types of orders:
- Market Order: Immediate trade execution at current market price
- Limit Order: Trade execution at a specified desired price
- Scale Order: Creation and execution of multiple limit orders within a set price range
- TWAP: Execution of trades by dividing one order into multiple orders at regular time intervals
For initial user acquisition, Hyperliquid implemented a free trading policy for the first 3 months after mainnet launch, after which they introduced a fee policy charging 0.25% to takers and providing a 0.2% rebate to makers. However, from March 2024, they switched to a tiered fee mechanism based on each wallet's 14-day trading volume, and restructured to a system where only market makers meeting certain trading volume thresholds can receive rebates.

The fee revenue generated in Hyperliquid is not collected by the team but is distributed to users who deposit liquidity in the HLP vault (Hyperliquid Liquidity Provider Vault) and to the assistance fund, which will be covered in more detail below.
Let's continue with detailed explanations of Hyperliquid DEX's specific operating mechanisms and characteristics.
2.2.1. Mark Price Mechanism
Since Hyperliquid is orderbook-based, users' buy/sell prices are fundamentally determined by the orderbook's liquidity. However, when orderbook liquidity is insufficient, price gaps with other markets can occur, and this can lead to liquidations, TP (Take Profit), and SL (Stop Loss) events being triggered by even small-scale liquidity attacks.
Additionally, due to the nature of perpetual futures trading without expiration dates, to control price divergence from spot prices, position holders must pay a certain amount to counter-position holders every specific time period (one hour in Hyperliquid's case) as funding rate. Therefore, Hyperliquid calculates a Mark Price based on external exchange price data for use in liquidations, TP/SL, and funding rate calculations. The weighting criteria for Hyperliquid's mark price calculation are as follows:
- Binance: 27.27%
- OKX: 18.18%
- Bybit: 18.18%
- Kraken: 9.09%
- Kucoin: 9.09%
- Gate IO: 9.09%
- MEXC: 9.09%
2.2.2. Derivatives and Spot Trading
Besides futures trading for specific tokens, Hyperliquid DEX provides trading for the following types of instruments:
- Index Perpetual Contracts: Provides perpetual futures trading for various blockchain ecosystem indices, such as an index tracking the average floor price of certain blue-chip NFT collections (NFTI-USD), and an index tracking the average Key price of the middle 8 accounts among the top 20 influencer accounts on the blockchain social platform Friend Tech (FRIEND-USD)
- Hyperps: A product supporting pre-trading for tokens not yet launched in the market, determining prices using the previous day's 8-hour exponential weighted moving average (EWMA) per minute rather than relying on specific prices
- Spot: Native tokens issued on the Hyperliquid network
Particularly among these, Hyperliquid has recently been putting significant effort into building and expanding its own ecosystem centered around native tokens and their spot trading, and Hyperliquid's native tokens continue to evolve through HIP (Hyperliquid Improvement Proposals).
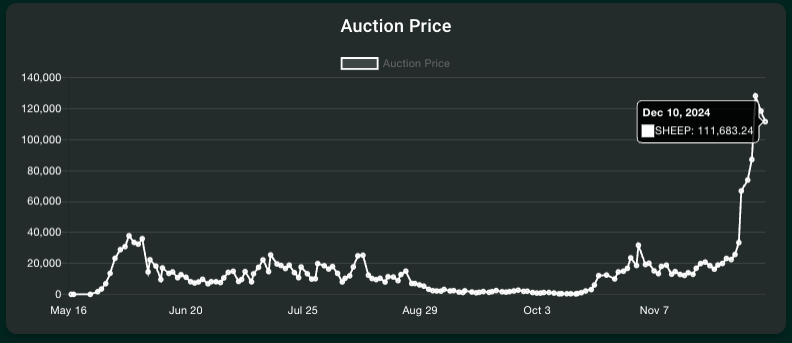
- HIP-1: A proposal for Hyperliquid native token issuance standards, including token standard formats and a Dutch Auction ticker auction system with 31-hour cycles to suppress disorderly token issuance. It also includes a Spot Dust feature that automatically submits sell orders to the orderbook once a day using tokens worth less than $1 held in users' wallets
- HIP-2: A proposal for solutions that automatically provide liquidity for issued native tokens. This solution submits buy/sell orders to the orderbook at ±0.3% of the current price every 3 seconds, and token issuers must choose whether to execute the liquidity provision solution and deposit the required liquidity when issuing tokens
As of December 4, 2024, a total of 53 tokens, including the network token $HYPE, are being traded on Hyperliquid DEX through the HIP standard. Spot trading volume increased dramatically after the launch of $HYPE, reaching a daily trading volume of $628M, and Hyperliquid's spot trading volume is expected to grow further as the number of issued tokens increases and more dApps that can utilize these tokens emerge. Currently, Hyperliquid's daily spot trading volume maintains $333M, slightly decreased after the $HYPE issuance.
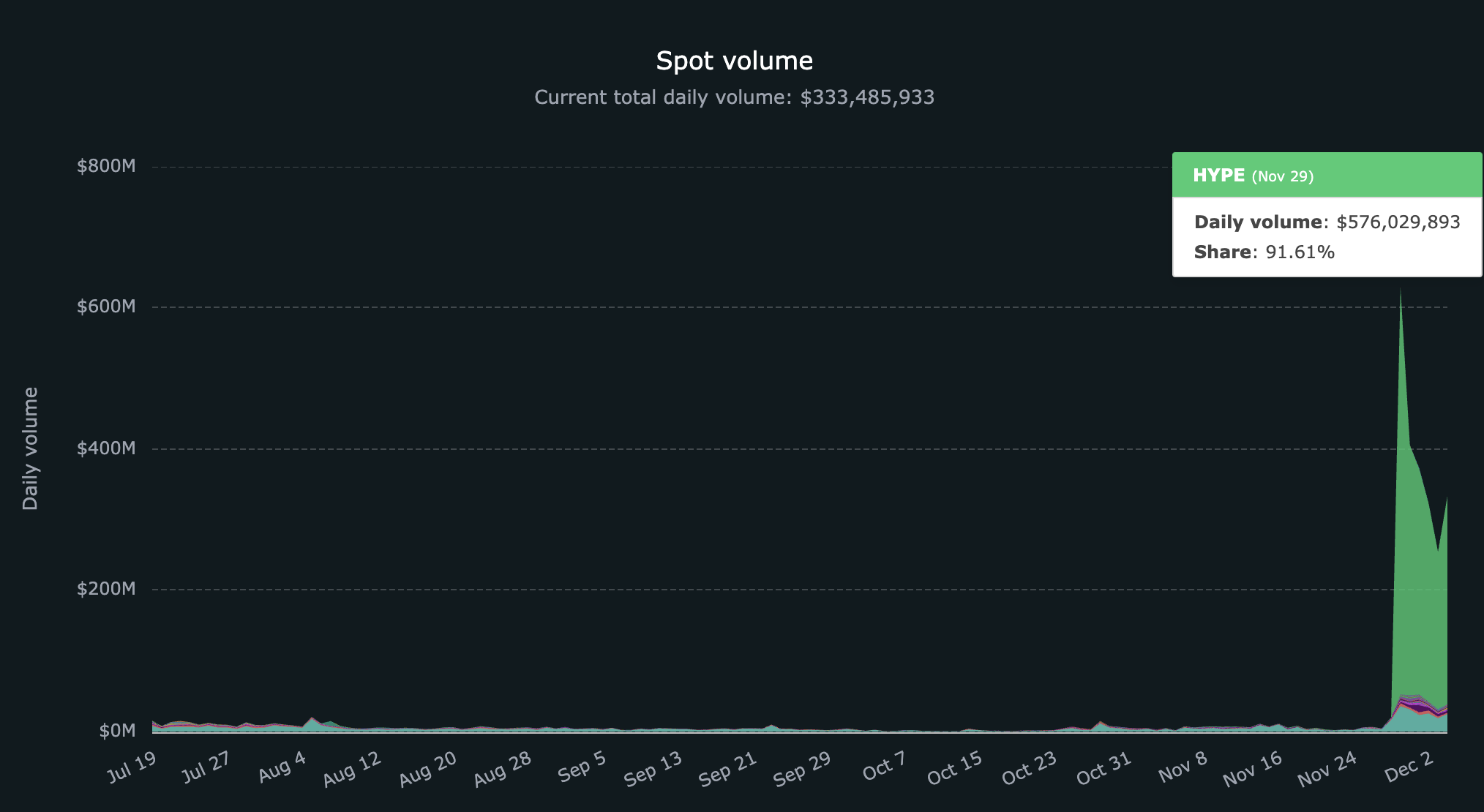
Additionally, as external liquidity flows into the Hyperliquid ecosystem and spot trading becomes more active after the issuance of $HYPE, the winning prices of token ticker auctions introduced through HIP-1 are also showing an upward trend.
2.2.3. HLP and User Vault
In existing orderbook-type exchanges, liquidity providers had to continuously monitor the orderbook and directly submit and modify buy/sell orders according to the situation, which meant they had to rely on a small number of professional market makers for liquidity provision, and as a result, these market makers monopolized the profits generated from liquidity provision.
In contrast, Hyperliquid provides a feature where users can participate in market making and earn profits simply by depositing assets in the HLP vault (Hyperliquid Liquidity Provider Vault), which executes liquidity provision to the Hyperliquid orderbook directly by the team. As explained earlier, most of Hyperliquid's revenue is distributed to users who deposit liquidity in the HLP.
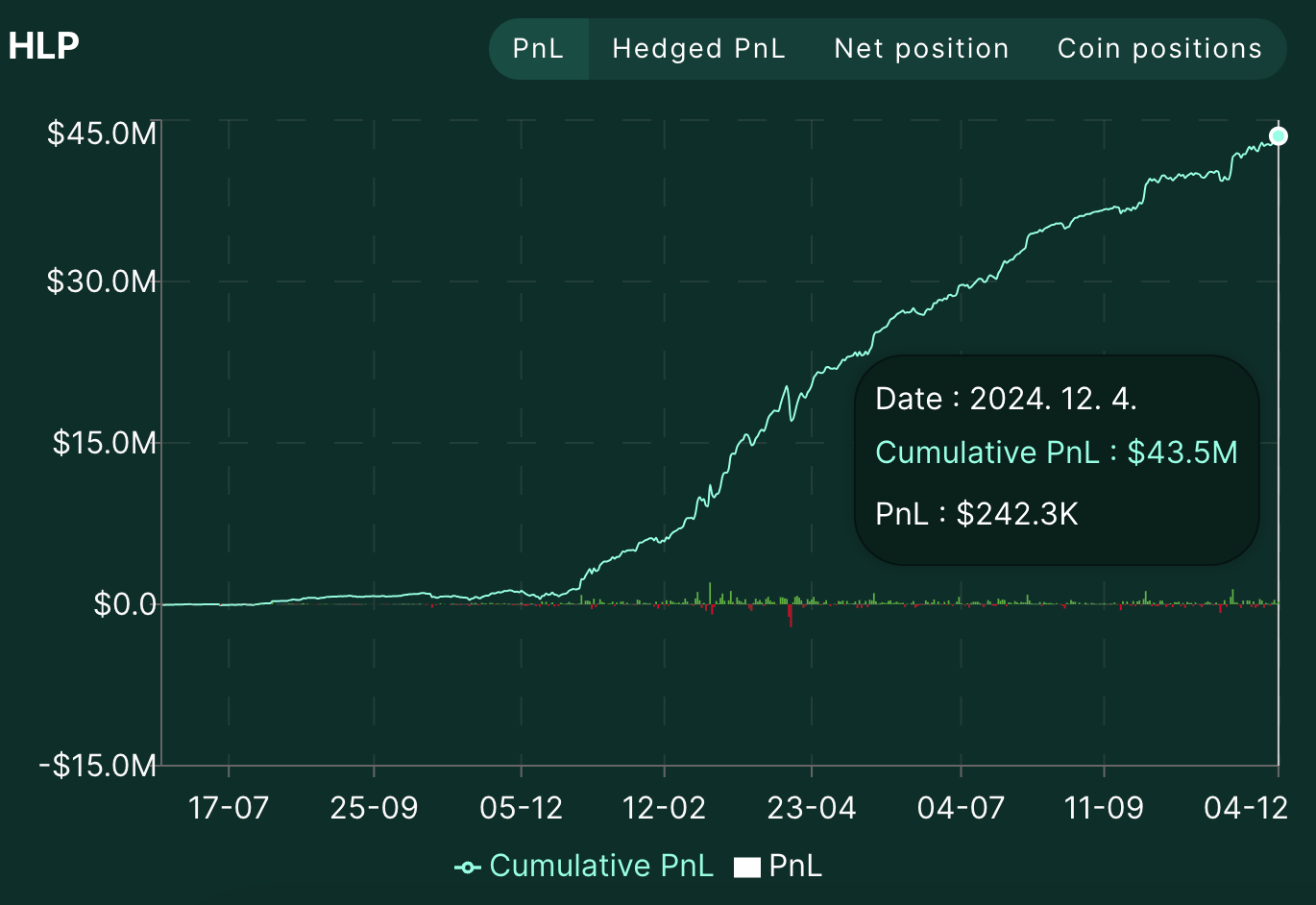
The HLP vault consists of three strategies: Strategy A, Strategy B, and Liquidator Strategy. The Liquidator Strategy works by taking over positions when the maintenance margin of liquidation targets falls below 2/3, while the specific operating mechanisms of the other two strategies are not disclosed to prevent exposure of operational details. However, since the order submission history and balance status of each strategy are recorded on the Hyperliquid network, they can be transparently checked through the HLP dashboard.
As of December 4, 2024, the total size of assets deposited in the HLP vault is $168M, with cumulative profits of $43M, recording an annual interest rate of approximately 20% for the month of November.
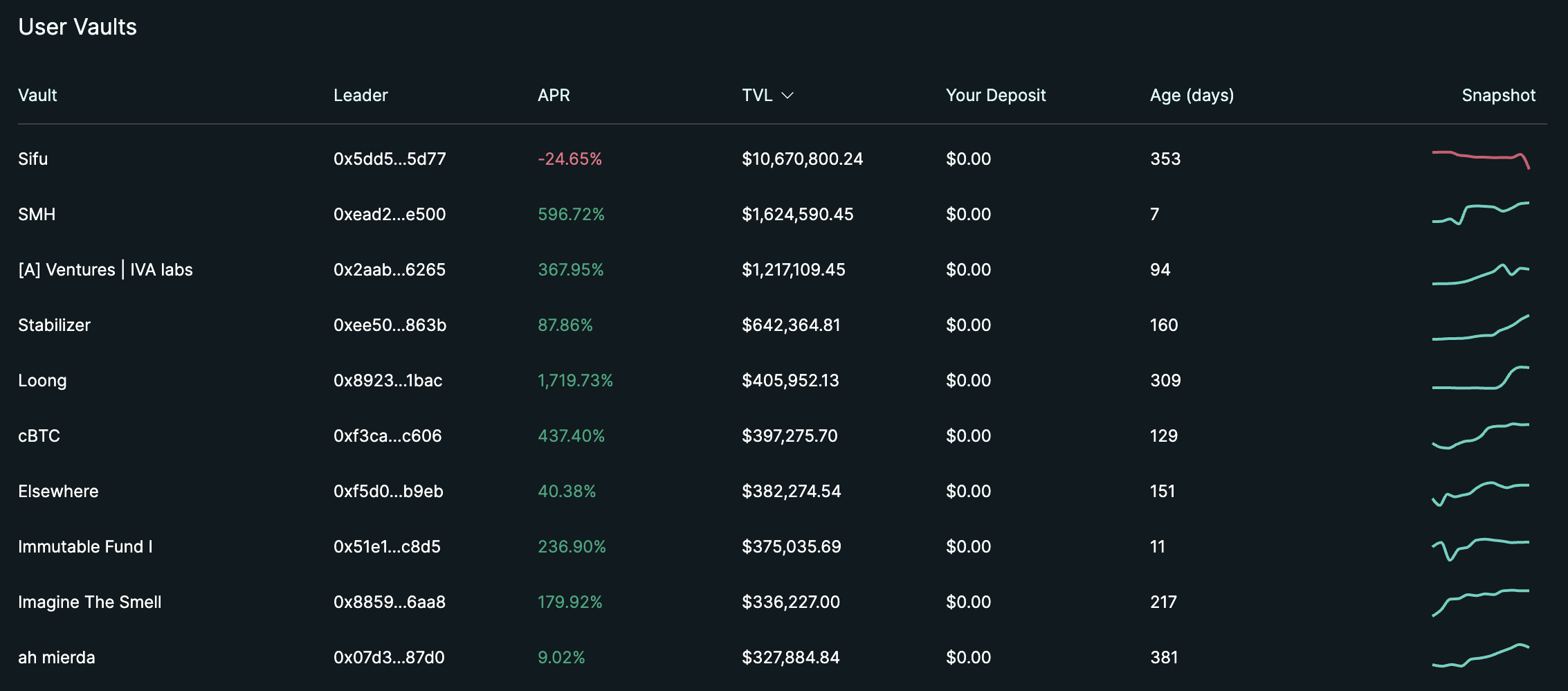
Additionally, Hyperliquid provides a User Vaults feature beyond HLP, allowing anyone to create vaults that execute trading strategies similar to HLP and accept user deposits for operation. Vault operators can receive 10% of profits generated through operation as performance fees, and must maintain their own asset ratio in the vault at 5% or higher to align interests with depositors.
2.3. $HYPE
From November 2022, its closed beta launch date, until September 2024, Hyperliquid distributed Hyperliquid points to users according to the following criteria:
- Closed Beta & Season 1 (2022.1~2024.4): Points distributed based on perpetual trading volume
- Season 2 (2024.6~2024.10): Points distributed for network ecosystem participation such as Layer 1 and spot trading
- Retroactively distributed points for trades in May, October, and November 2024
After the end of Season 2, on October 15, 2024, Hyperliquid established a foundation while simultaneously announcing the issuance and airdrop of the network token $HYPE, and on November 29, distributed $HYPE tokens equivalent to approximately 31% of total supply and 83% of initial circulation to users who had mined Hyperliquid points.
The utilities of $HYPE announced by the foundation along with the $HYPE issuance announcement are as follows:
- Utilize as security budget for HyperBFT through future introduction of $HYPE staking (currently being tested on testnet)
- Utilize as network fee token on the upcoming HyperEVM
- Utilize approximately 40% of total supply for future community incentives and ecosystem grants
After the token airdrop, $HYPE was listed on Hyperliquid's HYPE/USDC spot trading pair at a starting price of $2. The price increased approximately 7 times during the first 7 days after listing and continues to move sideways even in the correction phase.
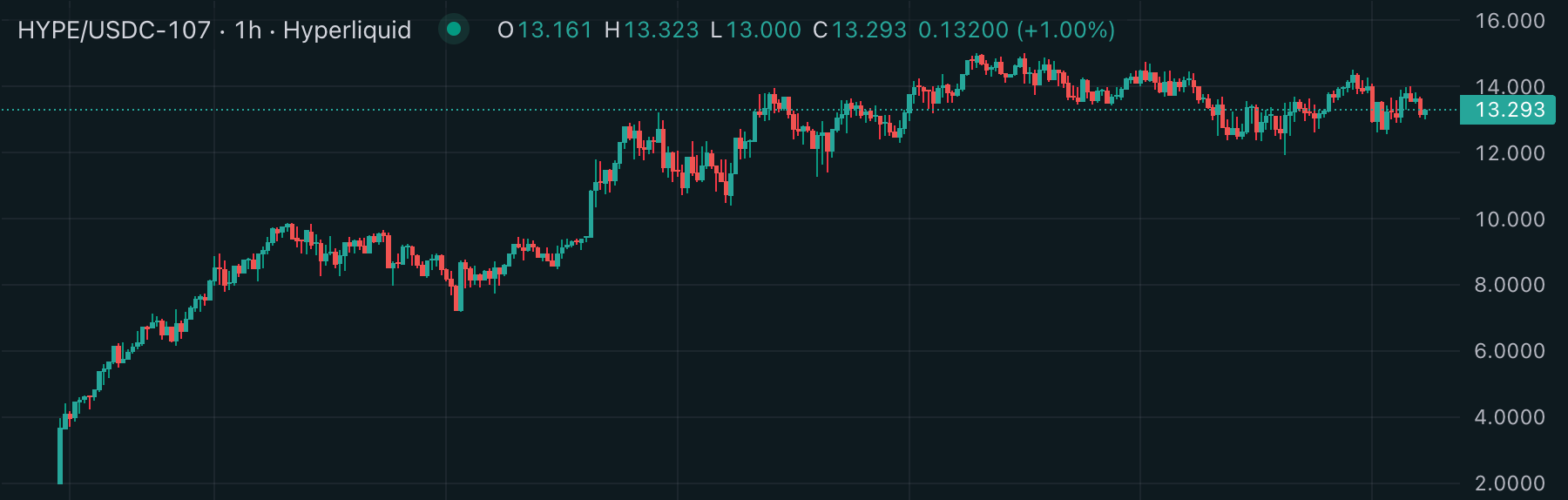
The factors driving this upward trend in $HYPE include: 1) the establishment of a solid community sharing the agenda of building an on-chain major exchange centered around the team, 2) the absence of institutional investors who could conduct large-scale selling due to proceeding with the project without external capital, and 3) continuous $HYPE buybacks using fees accumulated in the Hyperliquid assistance fund wallet.

3. Hyperliquid Ecosystem
Most orderbook-based Perpetual DEXes either lack their own network or, even if they have one, have a structure focused solely on 'trading' functionality, resulting in no cases where a subordinate ecosystem forms to create synergy effects with the Perpetual DEX. In contrast, Hyperliquid, as a Layer 1 network rather than just a Perpetual DEX, has a vision to build a massive ecosystem that combines existing on-chain users with centralized exchange-exclusive users by onboarding various dApps along with native tokens issued through HIP and the introduction of HyperEVM, creating network effects that existing Perpetual DEXes could not achieve.
3.1. $PURR
$PURR is Hyperliquid's first native token and meme coin, issued on April 16, 2024, with the introduction of HIP-1.
At issuance, 50% of the total circulation was distributed to Hyperliquid users proportional to their Hyperliquid points, and the remaining 50% was intended to be used for liquidity provision to the PURR/USDC spot pair according to HIP-2. However, after receiving feedback from the community that excessive liquidity was being supplied to the orderbook during testing, the team decided to burn 80% of the liquidity provision allocation. Additionally, with the introduction of a burn mechanism using part of the trading fees, continuous burning is taking place, resulting in a total of 401.8M $PURR burned so far, including the initial burn amount.
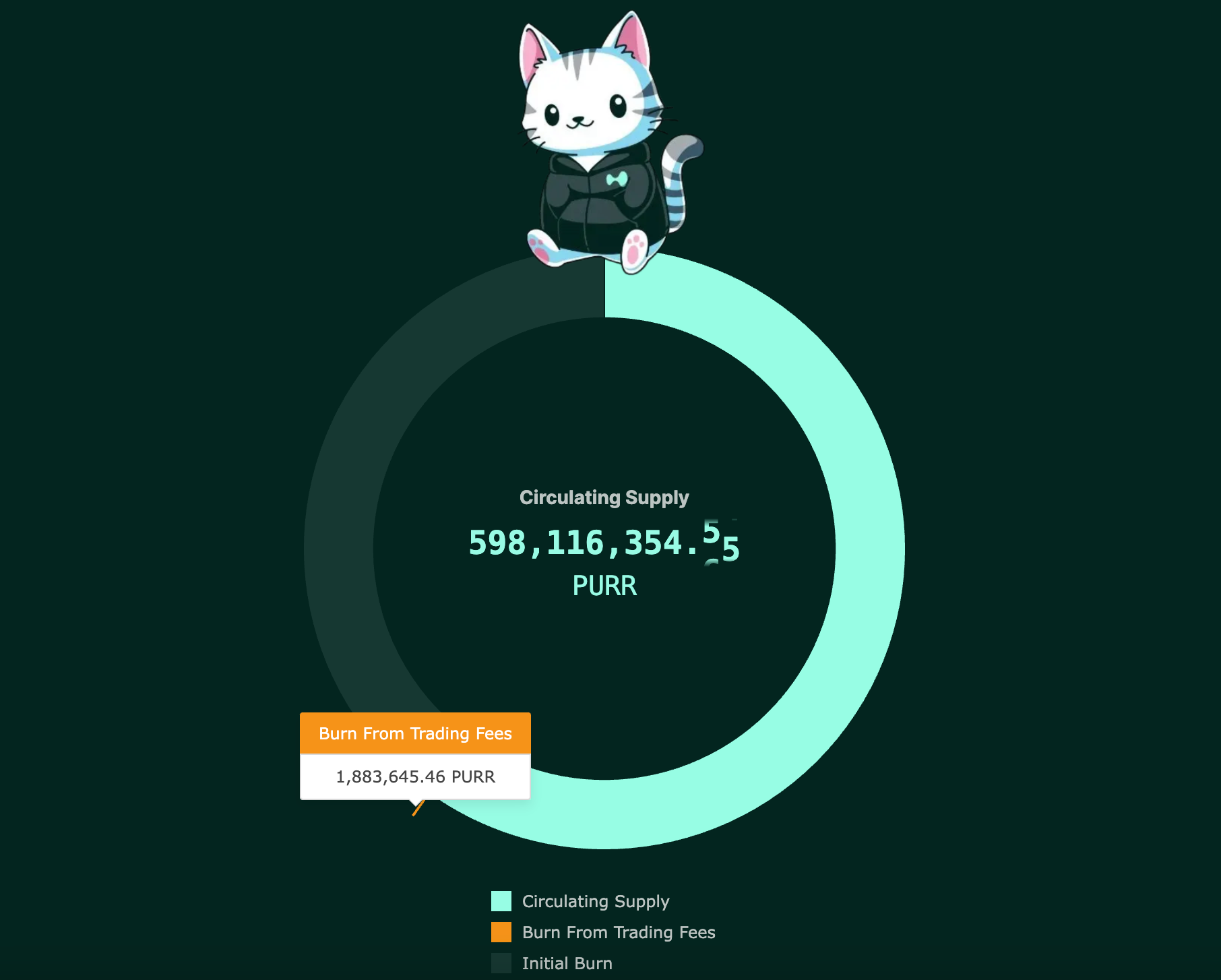
After $PURR's launch, as other native tokens established a trend of providing airdrops to $PURR holders, and rumors spread about Hyperliquid points being distributed to $PURR holders, $PURR's price recorded approximately 166% growth over three days starting from the day after launch. Recently, with external liquidity gathering in Hyperliquid alongside the $HYPE launch news, $PURR has also recorded significant gains, maintaining the second-highest market capitalization of $176M after $HYPE.
3.2. Hypurr Fun($HFUN)
Hypurr Fun is a Telegram bot that helps users trade on Hyperliquid through Telegram, and recently also launched and operates Hypurr Pump, a meme coin launchpad.
Users can easily create and close positions on Hyperliquid through the Telegram bot, participate in meme coin funding on Hypurr Pump, and meme coin projects that receive funding exceeding $100K on Hypurr Pump can participate in Hyperliquid ticker auctions to issue their meme coins based on the funding.
At the center of this project is $HFUN, the second native token issued on Hyperliquid after $PURR, which has a structure that burns $HFUN using platform revenue generated through Hypurr Fun and Hypurr Pump.
3.3. HyperLend
HyperLend is a lending protocol specialized for the Hyperliquid ecosystem, scheduled to launch alongside HyperEVM and currently operating only on the HyperEVM testnet.
The features HyperLend is preparing include:
- Leveraged Yield Farming: Providing leveraged yield farming positions using $stHYPE, the liquid staking token for $HYPE that Thunderhead, a liquid staking token issuance platform, plans to issue in the future
- HLP Collateral Loans: Providing loan services using funds deposited in HLP as collateral
- Vault Share Token Issuance: Issuing tokens that guarantee funds deposited in vaults and providing collateral loans for these tokens
- Cross-chain One-Click Loans: Bridge functionality for assets from various Layer 2 networks and adoption of these assets as HyperLend collateral
HyperLend, providing such features, is expected to diversify yield farming paths and enhance liquidity within the Hyperliquid ecosystem after launch by tokenizing various locked liquidity on Hyperliquid and providing loan functionality using this as collateral.
Additionally, the Hyperliquid ecosystem includes various protocols that are proceeding with or preparing to onboard from other networks, such as Abracadabra, which provides lending and leverage functionality based on the stablecoin $MIM, Rage Trade, a multi-chain perpetual aggregator, and Solv Protocol, a Bitcoin staking protocol. The activation of these protocols and native token issuance is expected to help increase trading volume on Hyperliquid DEX.
4. Conclusion
Unlike other Perpetual DEXes competing for limited liquidity while struggling with the dilemma of simultaneously satisfying both familiar trading experience and decentralization, Hyperliquid has implemented fast trading speeds and on-chain orderbooks without network fees and signatures. Additionally, with the launch of $HYPE as a turning point, it has received significant market attention and is showing rapid growth unprecedented among other Perpetual DEXes.
In particular, the spot token issuance mechanism introduced through HIP-1 serves as a token issuance launchpad, similar to Pump.fun on Solana, Clanker on Base, and Virtual Protocol, which have greatly contributed to increasing usage of recently popular networks. This creates a short-term effect of providing content to users flowing into the Hyperliquid network and increasing trading volume, and furthermore, is expected to contribute to forming a more expanded community beyond the current team-centered community.
Moreover, Hyperliquid aims to form an ecosystem by onboarding protocols that can utilize spot tokens beyond spot and futures trading functionality as a Layer 1. Through this, it has established itself as a leading player receiving expectations that it can bring centralized exchange-exclusive users, whom existing blockchain projects struggled to attract, onto the chain and build one massive ecosystem where they merge with existing on-chain users.
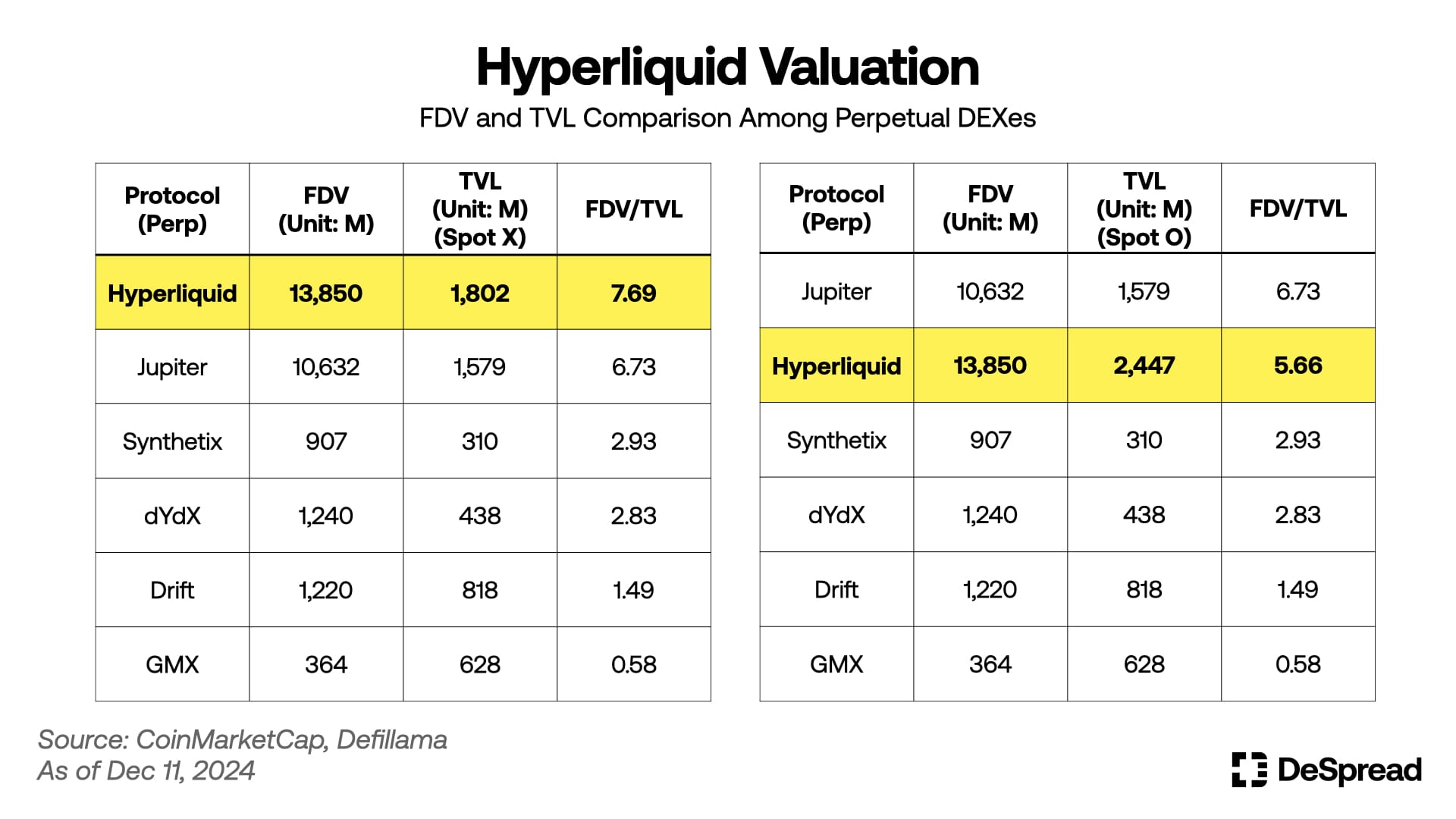
As mentioned in our 'Market Commentary | 12.06' article, there are opinions that Hyperliquid's token value might be somewhat overvalued due to its rapid growth after the token launch. However, considering that the figures presented in that article excluded the value of tokens existing in the Hyperliquid ecosystem (mainly tokens in the Spot market) for comparison between Perp DEXes, there's room to counter the overvaluation argument even in Perp DEX comparisons. As can be seen in the image above, when incorporating Spot market token values into TVL, the FDV/TVL ratio records '5.66', showing that it's actually in an undervalued range compared to Jupiter.
This valuation assessment can also be applied between Layer 1 projects, and can be briefly compared as follows (valuations based on DeFiLlama):
- Hyperliquid($HYPE)
- FDV: $13.85B / TVL: $2.45B
- FDV/TVL: 5.66
- Sui($SUI)
- FDV: $37B / TVL: $2.74B
- FDV/TVL: 13.5
- Aptos($APT)
- FDV: $13.1B / TVL: $2.48B
- FDV/TVL: 5.28
- Avalanche($AVAX)
- FDV: $31.8B / TVL: $2.57B
- FDV/TVL: 12.37
As shown in these comparisons, Hyperliquid appears to be in an undervalued range compared to Layer 1s with similar TVL metrics. Considering this, we believe there's potential for the project's value to be rated higher through the launch of HyperEVM and Layer 1 ecosystem expansion.
However, for Hyperliquid to achieve their vision and enhance project value, they face the challenge of smoothly implementing validator decentralization through $HYPE staking and introducing HyperEVM while maintaining current network performance, followed by the formation of an organic ecosystem centered around the community. Therefore, we should closely monitor the process of validator decentralization and HyperEVM introduction, as well as subsequent developments, to track and evaluate whether they can prove their proposed vision.